Retinoic acid protects human breast cancer cells against etoposide-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB-dependent but cIAP2-independent mechanisms
- PMID: 20102612
- PMCID: PMC2825243
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-15
Retinoic acid protects human breast cancer cells against etoposide-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB-dependent but cIAP2-independent mechanisms
Abstract
Background: Retinoids, through their cognate nuclear receptors, exert potent effects on cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis, and have significant promise for cancer therapy and chemoprevention. These ligands can determine the ultimate fate of target cells by stimulating or repressing gene expression directly, or indirectly through crosstalking with other signal transducers.
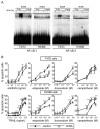
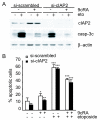
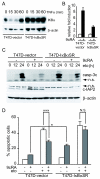
Results: Using different breast cancer cell models, we show here that depending on the cellular context retinoids can signal either towards cell death or cell survival. Indeed, retinoids can induce the expression of pro-apoptotic (i.e. TRAIL, TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand, Apo2L/TNFSF10) and anti-apoptotic (i.e. cIAP2, inhibitor of apoptosis protein-2) genes. Promoter mapping, gel retardation and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays revealed that retinoids induce the expression of this gene mainly through crosstalk with NF-kappaB. Supporting this crosstalk, the activation of NF-kappaB by retinoids in T47D cells antagonizes the apoptosis triggered by the chemotherapeutic drugs etoposide, camptothecin or doxorubicin. Notably apoptosis induced by death ligands (i.e. TRAIL or antiFAS) is not antagonized by retinoids. That knockdown of cIAP2 expression by small interfering RNA does not alter the inhibition of etoposide-induced apoptosis by retinoids in T47D cells reveals that stimulation of cIAP2 expression is not the cause of their anti-apoptotic action. However, ectopic overexpression of a NF-kappaB repressor increases apoptosis by retinoids moderately and abrogates almost completely the retinoid-dependent inhibition of etoposide-induced apoptosis. Our data exclude cIAP2 and suggest that retinoids target other regulator(s) of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway to induce resistance to etoposide on certain breast cancer cells.
Conclusions: This study shows an important role for the NF-kappaB pathway in retinoic acid signaling and retinoic acid-mediated resistance to cancer therapy-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells, independently of cIAP2. Our data support the use of NF-kappaB pathway activation as a marker for screening that will help to develop novel retinoids, or retinoid-based combination therapies with improved efficacy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential activity of GSK-3 isoforms regulates NF-κB and TRAIL- or TNFα induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Mar 27;5(3):e1142. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.102. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24675460 Free PMC article.
-
Up-Regulation of Glioma-Associated Oncogene Homolog 1 Expression by Serum Starvation Promotes Cell Survival in ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(5):1862-76. doi: 10.1159/000430156. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26182949
-
IRF-1 inhibits NF-κB activity, suppresses TRAF2 and cIAP1 and induces breast cancer cell specific growth inhibition.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(7):1029-41. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1046646. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26011589 Free PMC article.
-
Malt1 and cIAP2-Malt1 as effectors of NF-kappaB activation: kissing cousins or distant relatives?Cell Signal. 2010 Jan;22(1):9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.033. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 19772915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How retinoids regulate breast cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Jun;61(12):1475-84. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4002-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15197471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRPM8 ion channels differentially modulate proliferation and cell cycle distribution of normal and cancer prostate cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51825. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051825. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251635 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of IκBα at serine 32 by T-lymphokine-activated killer cell-originated protein kinase is essential for chemoresistance against doxorubicin in cervical cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 1;288(5):3585-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.422170. Epub 2012 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23250755 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of the effect of retinoic acids on the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 May;41(5):3499-507. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3212-8. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24615502
-
Breast cancer subtype dictates DNA methylation and ALDH1A3-mediated expression of tumor suppressor RARRES1.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):44096-44112. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9858. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27286452 Free PMC article.
-
RXR Ligands Negatively Regulate Thrombosis and Hemostasis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 May;37(5):812-822. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309207. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28254816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z, Sun G, Shen Z, Chen S, Chen Z. Differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans retinoic acid: 10-year experience of its clinical application. Chin Med J (Engl) 1999;112:963–967. - PubMed

