Integrin signaling through FAK in the regulation of mammary stem cells and breast cancer
- PMID: 20101634
- PMCID: PMC2848709
- DOI: 10.1002/iub.303
Integrin signaling through FAK in the regulation of mammary stem cells and breast cancer
Abstract
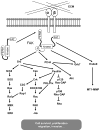
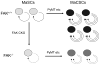
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase identified as a key mediator of intracellular signaling by integrins, a major family of cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix, in the regulation of different cellular functions in a variety of cells. Upon activation by integrins through disruption of an autoinhibitory mechanism, FAK undergoes autophosphorylation and forms a complex with Src and other cellular proteins to trigger downstream signaling through its kinase activity or scaffolding function. A number of integrins are identified as surface markers for mammary stem cells (MaSCs), and both integrins and FAK are found to play crucial roles in the maintenance of MaSCs in studies using mouse models, suggesting that integrin signaling through FAK may serve as a functional marker for MaSCs. Consistent with previous studies linking increased expression and activation of FAK to human breast cancer, these findings suggest a novel cellular mechanism of FAK promotion of mammary tumorigenesis by maintaining the pools of MaSCs as targets of oncogenic transformation. Furthermore, FAK inactivation in mouse models of breast cancer also reduced the pool of mammary cancer stem cells (MaCSCs), decreased their self-renewal in vitro, and compromised their tumorigenicity and maintenance in vivo, suggesting a potential role of integrin signaling through FAK in breast cancer growth and progression through its functions in MaCSCs. This review discusses these recent advances and future studies into the mechanism of integrin signaling through FAK in breast cancer through regulation of MaCSCs that may lead to development of novel therapies for this deadly disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Compensatory function of Pyk2 protein in the promotion of focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-null mammary cancer stem cell tumorigenicity and metastatic activity.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 27;286(21):18573-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.200717. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21471206 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009 Jun;28(1-2):35-49. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9165-4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009. PMID: 19169797 Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of the focal adhesion complex prevents oncogenic TGF-beta signaling and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R68. doi: 10.1186/bcr2360. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19740433 Free PMC article.
-
Function of focal adhesion kinase scaffolding to mediate endophilin A2 phosphorylation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mammary cancer stem cell activities in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 1;288(5):3322-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.420497. Epub 2012 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23255596 Free PMC article.
-
Role of focal adhesion kinase in integrin signaling.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997 Aug-Sep;29(8-9):1085-96. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(97)00051-4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9416004 Review.
Cited by
-
BRD4 modulates vulnerability of triple-negative breast cancer to targeting of integrin-dependent signaling pathways.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Dec;43(6):1049-1066. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00537-1. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 33006750 Free PMC article.
-
Id2 exerts tumor suppressor properties in lung cancer through its effects on cancer cell invasion and migration.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 2;12:801300. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.801300. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35982951 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin Heavy Chain Converter Domain Mutations Drive Early-Stage Changes in Extracellular Matrix Dynamics in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 16;10:894635. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.894635. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35784482 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of WD‑3 on tumor growth and the expression of integrin αvβ3 and ERK1/2 in mice bearing human gastric cancer using the 18F‑RGD PET/CT imaging system.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):9295-9300. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7827. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 29152665 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of TGF-β1 signaling by Matrigel via FAK signaling in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 1;11(1):7319. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86591-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33795740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Althuis MD, Dozier JM, Anderson WF, Devesa SS, Brinton LA. Global trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality 1973–1997. International journal of epidemiology. 2005;34:405–412. - PubMed
-
- Dalerba P, Cho RW, Clarke MF. Cancer stem cells: models and concepts. Annual review of medicine. 2007;58:267–284. - PubMed
-
- Wicha MS, Liu S, Dontu G. Cancer stem cells: an old idea--a paradigm shift. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1883–1890. discussion 1895–1886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

