Glucocorticoid receptor activates poised FKBP51 locus through long-distance interactions
- PMID: 20093418
- PMCID: PMC5419101
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0443
Glucocorticoid receptor activates poised FKBP51 locus through long-distance interactions
Abstract
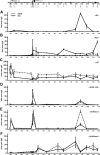
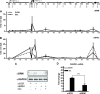
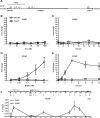
Recent studies have identified FKBP51 (FK506-binding protein 51) as a sensitive biomarker of corticosteroid responsiveness in vivo. In this work, we have elucidated the molecular mechanisms underlying the induction of FKBP51 by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in human A549 lung cancer cells showing robust accumulation of FKBP51 mRNA in response to dexamethasone exposure. Our quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation scans and enhancer activity analyses indicate that activation of the FKBP51 locus by glucocorticoids in vivo is triggered by the loading of GR to enhancers at about 34 kb 5' and about 87 kb 3' of the transcription start site. Interestingly, the region encompassing these enhancers is bordered by CCCTC-binding factor- and cohesin-binding sites. Dexamethasone treatment also decreased the histone density at several regions of the gene, which was paralleled with the occupancy of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes within the locus. Moreover, silencing of BRM subunit of the SWI/SNF complex blunted the glucocorticoid induction of the locus. The proximal promoter region along with the major intronic enhancer at approximately 87 kb, at which the GR binding peaked, had elevated levels of histone 3 acetylation and H3K4 trimethylation, whereas H3K36 trimethylation more generally marked the gene body and reflected the occupancy of RNA polymerase II. The occurrence of these active chromatin marks within the FKBP51 locus before glucocorticoid exposure suggests that it is poised for transcription in A549 cells. Taken together, these results indicate that the holo-GR is capable of activating transcription and evoking changes in chromatin structure through distant-acting enhancers.
Figures

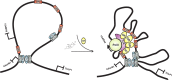
Similar articles
-
Long-range activation of FKBP51 transcription by the androgen receptor via distal intronic enhancers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(12):4135-48. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp352. Epub 2009 May 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19433513 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid resistance in squirrel monkeys results from a combination of a transcriptionally incompetent glucocorticoid receptor and overexpression of the glucocorticoid receptor co-chaperone FKBP51.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Jul;100(1-3):34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.03.004. Epub 2006 May 24. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16723223
-
Overexpression of the FK506-binding immunophilin FKBP51 is the common cause of glucocorticoid resistance in three New World primates.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2001 Nov;124(2):152-65. doi: 10.1006/gcen.2001.7696. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11703081
-
The FKBP51 Glucocorticoid Receptor Co-Chaperone: Regulation, Function, and Implications in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 5;18(12):2614. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122614. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29206196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recruitment of chromatin remodelling factors during gene activation via the glucocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):410-4. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961930 Review.
Cited by
-
The helix 1-3 loop in the glucocorticoid receptor LBD is a regulatory element for FKBP cochaperones.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Jul;27(7):1020-35. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1023. Epub 2013 May 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23686112 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced loss of DNA methylation in non-neuronal cells and potential involvement of DNMT1 in epigenetic regulation of Fkbp5.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Apr 13;420(3):570-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.035. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22445894 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory stimuli engage Brahma related gene 1 and Brahma in endothelial injury.Circ Res. 2013 Sep 27;113(8):986-96. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301296. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23963727 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid Receptor Binding Induces Rapid and Prolonged Large-Scale Chromatin Decompaction at Multiple Target Loci.Cell Rep. 2017 Dec 12;21(11):3022-3031. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.053. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29241532 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-Stress-Epigenetic Regulation of FKBP5: Clinical and Translational Implications.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Jan;41(1):261-74. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.235. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26250598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heitzer MD, Wolf IM, Sanchez ER, Witchel SF, DeFranco DB2007. Glucocorticoid receptor physiology. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 8:321–330 - PubMed
-
- Frankfurt O, Rosen ST2004. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid- induced apoptosis in hematologic malignancies: updates. Curr Opin Oncol 16:553–563 - PubMed
-
- Smoak KA, Cidlowski JA2004. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid receptor signaling during inflammation. Mech Ageing Dev 125:697–706 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

