Expression of a homeostatic regulator, Wip1 (wild-type p53-induced phosphatase), is temporally induced by c-Jun and p53 in response to UV irradiation
- PMID: 20093361
- PMCID: PMC2838327
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.070003
Expression of a homeostatic regulator, Wip1 (wild-type p53-induced phosphatase), is temporally induced by c-Jun and p53 in response to UV irradiation
Abstract
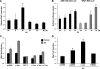
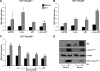
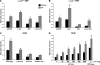
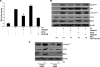
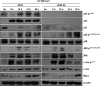
Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase (Wip1) is induced by p53 in response to stress, which results in the dephosphorylation of proteins (i.e. p38 MAPK, p53, and uracil DNA glycosylase) involved in DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoint pathways. p38 MAPK-p53 signaling is a unique way to induce Wip1 in response to stress. Here, we show that c-Jun directly binds to and activates the Wip1 promoter in response to UV irradiation. The binding of p53 to the promoter occurs earlier than that of c-Jun. In experiments, mutation of the p53 response element (p53RE) or c-Jun consensus sites reduced promoter activity in both non-stressed and stressed A549 cells. Overexpression of p53 significantly decreased Wip1 expression in HCT116 p53(+/+) cells but increased it in HCT116 p53(-/-) cells. Adenovirus-mediated p53 overexpression greatly decreased JNK activity. Up-regulation of Wip1 via the p38 MAPK-p53 and JNK-c-Jun pathways is specific, as demonstrated by our findings that p38 MAPK and JNK inhibitors affected the expression of the Wip1 protein, whereas an ERK inhibitor did not. c-Jun activation occurred much more quickly, and to a greater extent, in A549-E6 cells than in A549 cells, with delayed but fully induced Wip1 expression. These data indicate that Wip1 is activated via both the JNK-c-Jun and p38 MAPK-p53 signaling pathways and that temporal induction of Wip1 depends largely on the balance between c-Jun and p53, which compete for JNK binding. Moreover, our results suggest that JNK-c-Jun-mediated Wip1 induction could serve as a major signaling pathway in human tumors in response to frequent p53 mutation.
Figures
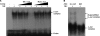


Similar articles
-
Loss of Wip1 sensitizes cells to stress- and DNA damage-induced apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jun 26;284(26):17428-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007823. Epub 2009 Apr 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19395378 Free PMC article.
-
p53-Independent expression of wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (Wip1) in methylmethane sulfonate-treated cancer cell lines and human tumors.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Jun;44(6):896-904. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.02.013. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22405851
-
Overexpression of the wip1 gene abrogates the p38 MAPK/p53/Wip1 pathway and silences p16 expression in human breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 Mar;101(3):269-78. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9304-y. Epub 2006 Aug 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. PMID: 16897432
-
Wip1 phosphatase: between p53 and MAPK kinases pathways.Oncotarget. 2016 May 24;7(21):31563-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7325. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26883196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The type 2C phosphatase Wip1: an oncogenic regulator of tumor suppressor and DNA damage response pathways.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008 Jun;27(2):123-35. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9127-x. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008. PMID: 18265945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging role and therapeutic implications of p53 in intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 1;9(1):433. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01730-5. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38040675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-targeting WIP1 and PARP induces synthetic lethality in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Mar 28;20(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00850-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35346236 Free PMC article.
-
Syk and IRAK1 Contribute to Immunopharmacological Activities of Anthraquinone-2-carboxlic Acid.Molecules. 2016 Jun 22;21(6):809. doi: 10.3390/molecules21060809. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27338330 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis serine protease Rv3668c can manipulate the host-pathogen interaction via Erk-NF-κB axis-mediated cytokine differential expression.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014 Sep;34(9):686-98. doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0071. Epub 2014 Mar 31. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014. PMID: 24684623 Free PMC article.
-
Feedbacks, Bifurcations, and Cell Fate Decision-Making in the p53 System.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Feb 29;12(2):e1004787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004787. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 26928575 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

