Monoclonal antibody-glial-derived neurotrophic factor fusion protein penetrates the blood-brain barrier in the mouse
- PMID: 20075191
- PMCID: PMC2845932
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.109.031534
Monoclonal antibody-glial-derived neurotrophic factor fusion protein penetrates the blood-brain barrier in the mouse
Abstract
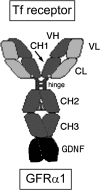
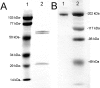
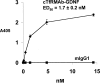
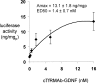
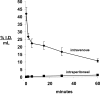
Glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a potent neuroprotective agent for multiple brain disorders, including Parkinson's disease. However, GDNF drug development is difficult because GDNF does not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To enable future drug development of GDNF in mouse models, the neurotrophin was re-engineered as an IgG fusion protein to enable penetration through the BBB after intravenous administration. The 134-amino acid GDNF was fused to the heavy chain of a chimeric monoclonal antibody (MAb) against the mouse transferrin receptor (TfR) designated the cTfRMAb. This antibody undergoes receptor-mediated transport across the BBB and acts as a molecular Trojan horse to ferry the GDNF into mouse brain. The cTfRMAb-GDNF fusion protein was expressed by stably transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells, affinity-purified, and the biochemical identity was confirmed by mouse IgG and GDNF Western blotting. The cTfRMAb-GDNF fusion protein was bifunctional and bound with high affinity to both the GDNF receptor alpha1, ED(50) = 1.7 +/- 0.2 nM, and the mouse TfR, ED(50) = 3.2 +/- 0.3 nM. The cTfRMAb-GDNF fusion protein was rapidly taken up by brain, and the brain uptake was 3.1 +/- 0.2% injected dose/g brain at 60 min after intravenous injection of a 1-mg/kg dose of the fusion protein. Brain capillary depletion analysis showed the majority of the fusion protein was transcytosed across the BBB with penetration into brain parenchyma. The brain uptake results indicate it is possible to achieve therapeutic elevations of GDNF in mouse brain with intravenous administration of the cTfRMAb-GDNF fusion protein.
Figures

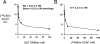
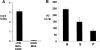
Similar articles
-
Re-engineering erythropoietin as an IgG fusion protein that penetrates the blood-brain barrier in the mouse.Mol Pharm. 2010 Dec 6;7(6):2148-55. doi: 10.1021/mp1001763. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Mol Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20860349
-
Pharmacokinetics and brain uptake of a genetically engineered bifunctional fusion antibody targeting the mouse transferrin receptor.Mol Pharm. 2010 Feb 1;7(1):237-44. doi: 10.1021/mp900235k. Mol Pharm. 2010. PMID: 19921848 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-penetrating tumor necrosis factor decoy receptor in the mouse.Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Jan;39(1):71-6. doi: 10.1124/dmd.110.036012. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011. PMID: 20884844 Free PMC article.
-
Reengineering biopharmaceuticals for targeted delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:269-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00011-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22230573 Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier drug delivery of IgG fusion proteins with a transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;12(2):207-22. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.952627. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25138991 Review.
Cited by
-
IgG Fusion Proteins for Brain Delivery of Biologics via Blood-Brain Barrier Receptor-Mediated Transport.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 15;14(7):1476. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071476. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Invasive Delivery of Therapeutics into the Brain: The Potential of Aptamers for Targeted Delivery.Biomedicines. 2020 May 14;8(5):120. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8050120. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32422973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Parkinson's disease with biologics that penetrate the blood-brain barrier via receptor-mediated transport.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 13;15:1276376. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1276376. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38035276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next generation antibody drugs: pursuit of the 'high-hanging fruit'.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Mar;17(3):197-223. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.227. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29192287 Review.
-
Intravenous treatment of experimental Parkinson's disease in the mouse with an IgG-GDNF fusion protein that penetrates the blood-brain barrier.Brain Res. 2010 Sep 17;1352:208-13. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.06.059. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20599807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Airavaara M, Planken A, Gäddnäs H, Piepponen TP, Saarma M, Ahtee L. (2004) Increased extracellular dopamine concentrations and FosB/ΔFosB expression in striatal brain areas of heterozygous GDNF knockout mice. Eur J Neurosci 20:2336–2344 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Fischer D, Henze C, Strenzke C, Westrich J, Ferger B, Höglinger GU, Oertel WH, Hartmann A. (2008) Characterization of the striatal 6-OHDA model of Parkinson's disease in wild type and α-synuclein-deleted mice. Exp Neurol 210:182–193 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
