Epigenetic regulation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency by virus-encoded microRNAs that target Rta and the cellular Rbl2-DNMT pathway
- PMID: 20071580
- PMCID: PMC2826065
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01997-09
Epigenetic regulation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency by virus-encoded microRNAs that target Rta and the cellular Rbl2-DNMT pathway
Abstract
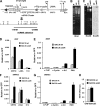
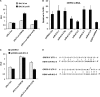
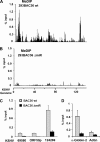
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) encodes a cluster of 12 microRNAs (miRNAs) that are processed from a transcript that is embedded within the major latency control region. We have generated a deletion mutation that eliminates 10 of the 12 viral miRNAs from the KSHV bacmid by using recombineering methods. The KSHV miRNA deletion mutant (BAC36 DeltamiR) behaved similarly to wild-type (wt) BAC36 in viral production, latency gene transcription, and viral DNA copy number in 293 and dermal microvascular endothelial cells (DMVECs). However, BAC36 DeltamiR consistently expressed elevated levels of viral lytic genes, including the immediate-early transcriptional activator Rta (ORF50). At least one KSHV microRNA (miRK12-5) was capable of suppressing ORF50 mRNA, but poor seed sequence alignments suggest that these targets may be indirect. Comparison of epigenetic marks in DeltamiR KSHV genomes revealed decreases in histone H3 K9 methylation, increases in histone H3 acetylation, and a striking loss of DNA methylation throughout the viral and cellular genome. One viral miRNA, K12-4-5p, was found to have a sequence targeting retinoblastoma (Rb)-like protein 2 (Rbl2), which is a known repressor of DNA methyl transferase 3a and 3b mRNA transcription. We show that ectopic expression of miR-K12-4-5p reduces Rbl2 protein expression and increases DNMT1, -3a, and -3b mRNA levels relative to the levels for control cells. We conclude that KSHV miRNA targets multiple pathways to maintain the latent state of the KSHV genome, including repression of the viral immediate-early protein Rta and a cellular factor, Rbl2, that regulates global epigenetic reprogramming.
Figures

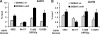
Similar articles
-
miR-K12-7-5p encoded by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus stabilizes the latent state by targeting viral ORF50/RTA.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 20;6(1):e16224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016224. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21283761 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Orf50 Transcripts: Discovery of New RTA Isoforms with Variable Transactivation Potential.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01434-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01434-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795414 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) by inhibitors of class III histone deacetylases: identification of sirtuin 1 as a regulator of the KSHV life cycle.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(11):6355-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00219-14. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24672028 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV miRNAs decrease expression of lytic genes in latently infected PEL and endothelial cells by targeting host transcription factors.Viruses. 2014 Oct 23;6(10):4005-23. doi: 10.3390/v6104005. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25341664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
Stealing the Show: KSHV Hijacks Host RNA Regulatory Pathways to Promote Infection.Viruses. 2020 Sep 14;12(9):1024. doi: 10.3390/v12091024. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32937781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral noncoding RNAs: more surprises.Genes Dev. 2015 Mar 15;29(6):567-84. doi: 10.1101/gad.259077.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25792595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shaping the host cell environment with viral noncoding RNAs.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 15;146:20-30. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.12.008. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36581481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-encoded microRNAs.Virology. 2011 Mar 15;411(2):325-43. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21277611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 Nef and KSHV oncogene K1 synergistically promote angiogenesis by inducing cellular miR-718 to regulate the PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Sep;42(15):9862-79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku583. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25104021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballestas, M. E., P. A. Chatis, and K. M. Kaye. 1999. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science 284:641-644. - PubMed
-
- Benetti, R., S. Gonzalo, I. Jaco, P. Munoz, S. Gonzalez, S. Schoeftner, E. Murchison, T. Andl, T. Chen, P. Klatt, E. Li, M. Serrano, S. Millar, G. Hannon, and M. A. Blasco. 2008. A mammalian microRNA cluster controls DNA methylation and telomere recombination via Rbl2-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferases. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15:268-279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buhler, M., and D. Moazed. 2007. Transcription and RNAi in heterochromatic gene silencing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14:1041-1048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

