Structure and biochemistry of cadherins and catenins
- PMID: 20066110
- PMCID: PMC2773639
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003053
Structure and biochemistry of cadherins and catenins
Abstract
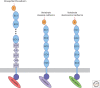
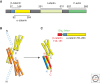
Classical cadherins mediate specific adhesion at intercellular adherens junctions. Interactions between cadherin ectodomains from apposed cells mediate cell-cell contact, whereas the intracellular region functionally links cadherins to the underlying cytoskeleton. Structural, biophysical, and biochemical studies have provided important insights into the mechanism and specificity of cell-cell adhesion by classical cadherins and their interplay with the cytoskeleton. Adhesive binding arises through exchange of beta strands between the first extracellular cadherin domains (EC1) of partner cadherins from adjacent cells. This "strand-swap" binding mode is common to classical and desmosomal cadherins, but sequence alignments suggest that other cadherins will bind differently. The intracellular region of classical cadherins binds to p120 and beta-catenin, and beta-catenin binds to the F-actin binding protein alpha-catenin. Rather than stably bridging beta-catenin to actin, it appears that alpha-catenin actively regulates the actin cytoskeleton at cadherin-based cell-cell contacts.
Figures
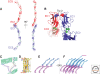
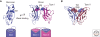

Similar articles
-
The three-dimensional structure of the cadherin-catenin complex.Subcell Biochem. 2012;60:39-62. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4186-7_3. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22674067 Review.
-
Structure and mechanism of cadherins and catenins in cell-cell contacts.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:237-61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104241. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17539752 Review.
-
Evolution of the cadherin-catenin complex.Subcell Biochem. 2012;60:9-35. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4186-7_2. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22674066 Review.
-
Cell adhesion. The minimal cadherin-catenin complex binds to actin filaments under force.Science. 2014 Oct 31;346(6209):1254211. doi: 10.1126/science.1254211. Science. 2014. PMID: 25359979 Free PMC article.
-
LI-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion does not require cytoplasmic interactions.J Cell Biol. 1997 Mar 10;136(5):1109-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.5.1109. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9060475 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The first Japanese family of CDH3-related hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Jun;9(6):e1688. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1688. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 33837674 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of αE-catenin-F-actin catch bond behavior.Elife. 2020 Sep 11;9:e60878. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60878. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32915141 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of ezrin/radixin/moesin mediates attractive growth cone guidance through regulation of growth cone actin and adhesion receptors.J Neurosci. 2012 Jan 4;32(1):282-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4794-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22219290 Free PMC article.
-
Cadherins as targets for genetic diseases.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Jan;2(1):a003095. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003095. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20182609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and canonical Wnt signaling.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Feb;2(2):a002915. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002915. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20182623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe K, Chisaka O, Van Roy F, Takeichi M 2004. Stability of dendritic spines and synaptic contacts is controlled by α-N-catenin. Nat Neurosci 7:357–363 - PubMed
-
- Aberle H, Schwartz H, Hoschuetzky H, Kemler R 1996. Single amino acid substitutions in proteins of the armadillo gene family abolish their binding to α-catenin. J Biol Chem 271:1520–1526 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
