Physiology and function of the tight junction
- PMID: 20066090
- PMCID: PMC2742087
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002584
Physiology and function of the tight junction
Abstract
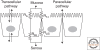
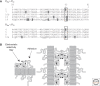
Understanding of tight junctions has evolved from their historical perception as inert solute barriers to recognition of their physiological and biochemical complexity. Many proteins are specifically localized to tight junctions, including cytoplasmic actin-binding proteins and adhesive transmembrane proteins. Among the latter are claudins, which are critical barrier proteins. Current information suggests that the paracellular barrier is most usefully modeled as having two physiologic components: a system of charge-selective small pores, 4 A in radius, and a second pathway created by larger discontinuities in the barrier, lacking charge or size discrimination. The first pathway is influenced by claudin expression patterns and the second is likely controlled by different proteins and signals. Recent information on claudin function and disease-causing mutations have led to a more complete understanding of their role in barrier formation, but progress is impeded by lack of high resolution structural information.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Charge-selective claudin channels.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Jun;1257:20-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06555.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22671585
-
[Claudins as tight junction proteins: the molecular element of paracellular transport].Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2013 Feb;99(2):175-95. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2013. PMID: 23650732 Review. Russian.
-
Computational Modeling of Claudin Structure and Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 23;21(3):742. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030742. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31979311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Claudin-21 Has a Paracellular Channel Role at Tight Junctions.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jan 4;36(6):954-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00758-15. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26729464 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring size-dependent permeability of the tight junction using PEG profiling.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;762:1-11. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-185-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21717345
Cited by
-
Contribution of immunomodulators to gastroesophageal reflux disease and its complications: stromal cells, interleukin 4, and adiponectin.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016 Sep;1380(1):183-194. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13157. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016. PMID: 27441783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tight junction CLDN2 gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 27;5:10642. doi: 10.1038/srep10642. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26212084 Free PMC article.
-
The N and C termini of ZO-1 are surrounded by distinct proteins and functional protein networks.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13775-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.466193. Epub 2013 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23553632 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacteria isolated from infants and cultured on human milk oligosaccharides affect intestinal epithelial function.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012 Sep;55(3):321-7. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31824fb899. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22383026 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Inflammation Contributes to Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis.JID Innov. 2022 Apr 26;2(5):100131. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2022.100131. eCollection 2022 Sep. JID Innov. 2022. PMID: 36059592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexandre MD, Lu Q, Chen YH 2005. Overexpression of claudin-7 decreases the paracellular Cl− conductance and increases the paracellular Na+ conductance in LLC-PK1 cells. J Cell Sci 118:2683–2693 - PubMed
-
- Amasheh S, Meiri N, Gitter AH, Schoneberg T, Mankertz J, Schulzke JD, Fromm M 2002. Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 115:4969–4976 - PubMed
-
- Amasheh S, Schmidt T, Mahn M, Florian P, Mankertz J, Tavalali S, Gitter AH, Schulzke JD, Fromm M 2005. Contribution of claudin-5 to barrier properties in tight junctions of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 321:89–96 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
