The RABIT: a rapid automated biodosimetry tool for radiological triage
- PMID: 20065685
- PMCID: PMC2923588
- DOI: 10.1097/HP.0b013e3181ab3cb6
The RABIT: a rapid automated biodosimetry tool for radiological triage
Abstract
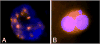
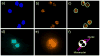
In response to the recognized need for high throughput biodosimetry methods for use after large-scale radiological events, a logical approach is complete automation of standard biodosimetric assays that are currently performed manually. The authors describe progress to date on the RABIT (Rapid Automated BIodosimetry Tool), designed to score micronuclei or gamma-H2AX fluorescence in lymphocytes derived from a single drop of blood from a fingerstick. The RABIT system is designed to be completely automated, from the input of the capillary blood sample into the machine to the output of a dose estimate. Improvements in throughput are achieved through use of a single drop of blood, optimization of the biological protocols for in situ analysis in multi-well plates, implementation of robotic-plate and liquid handling, and new developments in high-speed imaging. Automating well-established bioassays represents a promising approach to high-throughput radiation biodosimetry, both because high throughputs can be achieved, but also because the time to deployment is potentially much shorter than for a new biological assay. Here the authors describe the development of each of the individual modules of the RABIT system and show preliminary data from key modules. System integration is ongoing, followed by calibration and validation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The RABiT: a rapid automated biodosimetry tool for radiological triage. II. Technological developments.Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Aug;87(8):776-90. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2011.573612. Epub 2011 May 11. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011. PMID: 21557703 Free PMC article.
-
THE DECADE OF THE RABiT (2005-15).Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2016 Dec;172(1-3):201-206. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncw172. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2016. PMID: 27412510 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Triage Radiation Biodosimetry: Integrating Imaging Flow Cytometry with High-Throughput Robotics to Perform the Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay.Radiat Res. 2019 Apr;191(4):342-351. doi: 10.1667/RR15243.1. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 30779694 Free PMC article.
-
Potential application of γ-H2AX as a biodosimetry tool for radiation triage.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021 Jan-Jun;787:108350. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2020.108350. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021. PMID: 34083048 Review.
-
Advances in in vivo EPR Tooth BIOdosimetry: Meeting the targets for initial triage following a large-scale radiation event.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2016 Dec;172(1-3):72-80. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncw165. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2016. PMID: 27421468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Framework for Comparative Evaluation of Dosimetric Methods to Triage a Large Population Following a Radiological Event.Radiat Meas. 2011 Sep 1;46(9):916-922. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2011.02.019. Radiat Meas. 2011. PMID: 21949481 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the principles and practice of biodosimetry.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2014 May;53(2):221-32. doi: 10.1007/s00411-014-0522-0. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24519326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The production and composition of rat sebum is unaffected by 3 Gy gamma radiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Apr;87(4):360-71. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2010.537432. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011. PMID: 21158499 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in the use of γ-H2AX as a quantitative DNA double-strand break biomarker.Aging (Albany NY). 2011 Feb;3(2):168-74. doi: 10.18632/aging.100284. Aging (Albany NY). 2011. PMID: 21325706 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Strategies in the Development of Radiation Biodosimetry Tests for Patient Management.Radiat Res. 2021 Nov 1;196(5):455-467. doi: 10.1667/RADE-21-00072.1. Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 34143223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blakely WF, Carr Z, Chu MC, Dayal-Drager R, Fujimoto K, Hopmeir M, Kulka U, Lillis-Hearne P, Livingston G, Lloyd DC, Maznyk N, Perez Mdel R, Romm H, Takashima Y, Voisin P, Wilkins RC, Yoshida MA. WHO 1st consultation on the development of a Global Biodosimetry Laboratories Network for radiation emergencies (BioDoseNet) Radiat Res. 2009;171:127–139. - PubMed
-
- Blakely WF, Prasanna PGS, Grace MB, Miller AC. Radiation exposure assessment using cytological and molecular biomarkers. Radiat Protec Dosim. 2001;97:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Castleman KR, Schulze M, Wu Q. Automated biodosimetry using digital image analysis of fluorescence in situ hybridization specimens. Radiat Res. 1997;148:S71–S75. - PubMed
-
- da Cruz AD, McArthur AG, Silva CC, Curado MP, Glickman BW. Human micronucleus counts are correlated with age, smoking, and cesium-137 dose in the Goiânia (Brazil) radiological accident. Mutat Res. 1994;313:57–68. - PubMed
-
- Decordier I, Papine A, Plas G, Roesems S, Vande Loock K, Moreno-Palomo J, Cemeli E, Anderson D, Fucic A, Marcos R, Soussaline F, Kirsch-Volders M. Automated image analysis of cytokinesis-blocked micronuclei: an adapted protocol and a validated scoring procedure for biomonitoring. Mutagenesis. 2009;24:85–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

