Upregulated IL-21 and IL-21 receptor expression is involved in experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU)
- PMID: 20057909
- PMCID: PMC2802297
Upregulated IL-21 and IL-21 receptor expression is involved in experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU)
Abstract
Purpose: Interleukin (IL)-21 has recently been shown to play a vital role in the development of many autoimmune diseases. Our study is designed to investigate the alteration and possible function of IL-21 in the development of an experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) model.
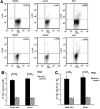
Methods: EAU was induced in B10.RIII mice by subcutaneous injection of interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) 161-180 emulsified with complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) and evaluated by clinical and histopathologic observation. IL-21 and IL-21R mRNA expressions in cells of draining lymph node (DLN) and spleen in EAU and control mice were determined by reverse transcription-PCR. The frequencies of interleukin-21 receptor positive cells were also examined using flow cytometry. IL-17 levels in the supernatant of the cell culture upon IL-21 stimulation were assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
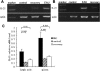
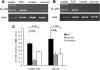
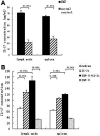
Results: Results showed that EAU was successfully induced by IRBP161-180. Expression of IL-21 mRNA was significantly increased in cells of DLN and spleen in EAU compared with recovery phase mice and normal controls. IL-21R was also found upregulated in DLN and spleen cells of EAU mice by reverse transcription-PCR and flow cytometry. Cells in EAU cultured with IL-21 combined with transforming growth factor-beta induced increased production of IL-17.
Conclusion: The findings revealed that increased IL-21 and IL-21R expression may be involved in the development of EAU, possibly by promoting IL-17 secretion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Upregulation of DR3 expression in CD4⁺ T cells promotes secretion of IL-17 in experimental autoimmune uveitis.Mol Vis. 2011;17:3486-93. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22219644 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Th1 and Th2 cells in lymph nodes and spleens of mice during experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2001 Sep-Oct;45(5):463-9. doi: 10.1016/s0021-5155(01)00369-0. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2001. PMID: 11583666
-
CTLA4-Ig suppresses development of experimental autoimmune uveitis in the induction and effector phases: Comparison with blockade of interleukin-6.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Nov;140:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.08.012. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 26297802
-
Activation of liver X receptor alleviates ocular inflammation in experimental autoimmune uveitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Apr 28;55(4):2795-804. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13323. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24699378 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of retinoic acid receptor-alpha/beta-specific ligand Am80 suppresses experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Mar 1;52(3):1548-56. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5963. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 20861477
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic effect of specific T cells from mice with experimental autoimmune uveitis on murine photoreceptor cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2020 Aug 18;13(8):1180-1186. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2020.08.02. eCollection 2020. Int J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32821670 Free PMC article.
-
CFH 184G as a genetic risk marker for anterior uveitis in Chinese females.Mol Vis. 2011;17:2655-64. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22065918 Free PMC article.
-
Serum IL-21 levels associated with chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis B-related liver failure.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Apr;7(4):1013-1019. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1533. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24669269 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines that Modulate the Differentiation of Th17 Cells in Autoimmune Uveitis.J Immunol Res. 2021 Mar 16;2021:6693542. doi: 10.1155/2021/6693542. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33816637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of molecular genetics in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease.J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2014 Jul 22;4:20. doi: 10.1186/s12348-014-0020-1. eCollection 2014. J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect. 2014. PMID: 25097674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tarrant TK, Silver PB, Chan CC, Wiggert B, Caspi RR. Endogenous IL-12 is required for induction and expression of experimental autoimmune uveitis. J Immunol. 1998;161:122–7. - PubMed
-
- Tarrant TK, Silver PB, Wahlsten JL, Rizzo LV, Chan CC, Wiggert B, Caspi RR. Interleukin 12 protects from a T helper type 1-mediated autoimmune disease, experimental autoimmune uveitis, through a mechanism involving interferon gamma, nitric oxide, and apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1999;189:219–30. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jones LS, Rizzo LV, Agarwal RK, Tarrant TK, Chan CC, Wiggert B, Caspi RR. IFN-gamma-deficient mice develop experimental autoimmune uveitis in the context of a deviant effector response. J Immunol. 1997;158:5997–6005. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
