Breadth of neutralizing antibodies elicited by stable, homogeneous clade A and clade C HIV-1 gp140 envelope trimers in guinea pigs
- PMID: 20053749
- PMCID: PMC2838122
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02252-09
Breadth of neutralizing antibodies elicited by stable, homogeneous clade A and clade C HIV-1 gp140 envelope trimers in guinea pigs
Abstract
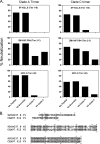
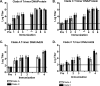
The native envelope (Env) spike on the surface of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is trimeric, and thus trimeric Env vaccine immunogens are currently being explored in preclinical immunogenicity studies. Key challenges have included the production and purification of biochemically homogeneous and stable trimers and the evaluation of these immunogens utilizing standardized virus panels for neutralization assays. Here we report the binding and neutralizing antibody (NAb) responses elicited by clade A (92UG037.8) and clade C (CZA97.012) Env gp140 trimer immunogens in guinea pigs. These trimers have been selected and engineered for optimal biochemical stability and have defined antigenic properties. Purified gp140 trimers with Ribi adjuvant elicited potent, cross-clade NAb responses against tier 1 viruses as well as detectable but low-titer NAb responses against select tier 2 viruses from clades A, B, and C. In particular, the clade C trimer elicited NAbs that neutralized 27%, 20%, and 47% of tier 2 viruses from clades A, B, and C, respectively. Heterologous DNA prime, protein boost as well as DNA prime, recombinant adenovirus boost regimens expressing these antigens, however, did not result in an increased magnitude or breadth of NAb responses in this system. These data demonstrate the immunogenicity of stable, homogeneous clade A and clade C gp140 trimers and exemplify the utility of standardized tier 1 and tier 2 virus panels for assessing the NAb responses of candidate HIV-1 Env immunogens.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A multivalent clade C HIV-1 Env trimer cocktail elicits a higher magnitude of neutralizing antibodies than any individual component.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2507-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03331-14. Epub 2014 Dec 24. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25540368 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing Antibody Responses following Long-Term Vaccination with HIV-1 Env gp140 in Guinea Pigs.J Virol. 2018 Jun 13;92(13):e00369-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00369-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29643249 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of a Prefusion HIV-1 Envelope Trimer in Complex with a Quaternary-Structure-Specific Antibody.J Virol. 2015 Dec 30;90(6):2740-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02380-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26719262 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Envelope Trimer Design and Immunization Strategies To Induce Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies.Trends Immunol. 2016 Mar;37(3):221-232. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Trends Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26869204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for inducing effective neutralizing antibody responses against HIV-1.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019 Nov;18(11):1127-1143. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2019.1690458. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019. PMID: 31791150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 envelope trimer elicits more potent neutralizing antibody responses than monomeric gp120.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 24;109(30):12111-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204533109. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22773820 Free PMC article.
-
Polyvalent AIDS vaccines.Curr HIV Res. 2010 Dec;8(8):622-9. doi: 10.2174/157016210794088290. Curr HIV Res. 2010. PMID: 21054250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influences on the Design and Purification of Soluble, Recombinant Native-Like HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Trimers.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(23):12189-210. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01768-15. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26311893 Free PMC article.
-
DNA prime/protein boost vaccination elicits robust humoral response in rhesus macaques using oligomeric simian immunodeficiency virus envelope and Advax delta inulin adjuvant.J Gen Virol. 2017 Aug;98(8):2143-2155. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000863. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Gen Virol. 2017. PMID: 28758637 Free PMC article.
-
A Cysteine Zipper Stabilizes a Pre-Fusion F Glycoprotein Vaccine for Respiratory Syncytial Virus.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 22;10(6):e0128779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128779. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26098893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbink, P., A. A. Lemckert, B. A. Ewald, D. M. Lynch, M. Denholtz, S. Smits, L. Holterman, I. Damen, R. Vogels, A. R. Thorner, K. L. O'Brien, A. Carville, K. G. Mansfield, J. Goudsmit, M. J. Havenga, and D. H. Barouch. 2007. Comparative seroprevalence and immunogenicity of six rare serotype recombinant adenovirus vaccine vectors from subgroups B and D. J. Virol. 81:4654-4663. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beddows, S., M. Franti, A. K. Dey, M. Kirschner, S. P. Iyer, D. C. Fisch, T. Ketas, E. Yuste, R. C. Desrosiers, P. J. Klasse, P. J. Maddon, W. C. Olson, and J. P. Moore. 2007. A comparative immunogenicity study in rabbits of disulfide-stabilized, proteolytically cleaved, soluble trimeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp140, trimeric cleavage-defective gp140 and monomeric gp120. Virology 360:329-340. - PubMed
-
- Berger, E. A., P. M. Murphy, and J. M. Farber. 1999. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:657-700. - PubMed
-
- Berman, P. W., D. J. Eastman, D. M. Wilkes, G. R. Nakamura, T. J. Gregory, D. Schwartz, G. Gorse, R. Belshe, M. L. Clements, and R. A. Byrn. 1994. Comparison of the immune response to recombinant gp120 in humans and chimpanzees. AIDS 8:591-601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

