Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-1 in cerebral microvessels changes during development and influences urocortin transport across the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 20032050
- PMCID: PMC2840693
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1039
Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-1 in cerebral microvessels changes during development and influences urocortin transport across the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
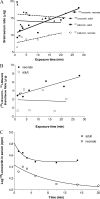
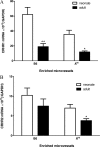
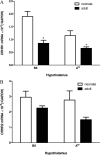
In this study we tested the hypothesis that receptor-mediated transport of urocortin across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) undergoes developmental changes. Urocortin is a peptide produced by both selective brain regions and peripheral organs, and it is involved in feeding, memory, mood, cardiovascular functions, and immune regulation. In BBB studies with multiple-time regression analysis, we found that neonatal mice had a significant influx of (125)I-urocortin. By contrast, adult mice did not transport urocortin across the BBB. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor (CRHR)-1 was developmentally regulated in enriched cerebral microvessels as well as hypothalamus, being significantly higher in neonatal than adult mice. This change was less dramatic in agouti viable yellow mice, a strain that develops adult-onset obesity. The level of expression of CRHR1 mRNA was 33-fold higher in the microvessels than in hypothalamic homogenates. The mRNA for CRHR2 was less abundant in both regions and less prone to changes with development or the agouti viable yellow mutation. Supported by previous findings of receptor-mediated endocytosis of urocortin, these results suggest that permeation of urocortin across the BBB is dependent on the level of CRHR1 expression in cerebral microvessels. These novel findings of differential regulation of CRH receptor subtypes help elucidate developmental processes in the brain, particularly for the urocortin system.
Figures
Comment in
-
Gut-brain communications: not the same at all ages.Endocrinology. 2010 Mar;151(3):852-4. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1442. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20172973 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor (CRHR)1 and CRHR2 are both trafficking and signaling receptors for urocortin.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Mar;21(3):700-11. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0503. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17170072
-
Modulation of feeding-related peptide/protein signals by the blood-brain barrier.J Neurochem. 2004 Jul;90(2):455-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02502.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15228601
-
Expression of urocortin and its receptors in the rat epididymis.Reprod Biol. 2014 Apr;14(2):140-7. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2014.01.007. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Reprod Biol. 2014. PMID: 24856473
-
Urocortin and the brain.Prog Neurobiol. 2008 Feb;84(2):148-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2007.10.008. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Prog Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18078706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Milestones in CRH Research.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017;10(4):259-263. doi: 10.2174/1874467210666170109165219. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28071586 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for CRHR1 in multiple sclerosis using supervised machine learning and meta-analysis in 12,566 individuals.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Nov 1;19(21):4286-95. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq328. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20699326 Free PMC article.
-
Common variants at 6q22 and 17q21 are associated with intracranial volume.Nat Genet. 2012 Apr 15;44(5):539-44. doi: 10.1038/ng.2245. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22504418 Free PMC article.
-
Common variants at 12q15 and 12q24 are associated with infant head circumference.Nat Genet. 2012 Apr 15;44(5):532-538. doi: 10.1038/ng.2238. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22504419 Free PMC article.
-
Urocortin Treatment Improves Acute Hemodynamic Instability and Reduces Myocardial Damage in Post-Cardiac Arrest Myocardial Dysfunction.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 10;11(11):e0166324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166324. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27832152 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-brain communications: not the same at all ages.Endocrinology. 2010 Mar;151(3):852-4. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1442. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20172973 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V, Pan W 2000 Activation of urocortin transport into brain by leptin. Peptides 21:1811–1817 - PubMed
-
- Kastin AJ, Pan W, Akerstrom V, Hackler L, Wang C, Kotz CM 2002 Novel peptide-peptide cooperation may transform feeding behavior. Peptides 23:2189–2196 - PubMed
-
- Pan W, Akerstrom V, Zhang J, Pejovic V, Kastin AJ 2004 Modulation of feeding-related peptide/protein signals by the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem 90:455–461 - PubMed
-
- Tu H, Kastin AJ, Pan W 2007 CRH-R1 and CRH-R2 are both trafficking and signaling receptors for urocortin. Mol Endocrinol 21:700–711 - PubMed

