Active immunization to tumor necrosis factor-alpha is effective in treating chronic established inflammatory disease: a long-term study in a transgenic model of arthritis
- PMID: 20030816
- PMCID: PMC3003505
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2897
Active immunization to tumor necrosis factor-alpha is effective in treating chronic established inflammatory disease: a long-term study in a transgenic model of arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Passive blockade of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) has demonstrated high therapeutic efficiency in chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, although some concerns remain such as occurrence of resistance and high cost. These limitations prompted investigations of an alternative strategy to target TNF-alpha. This study sought to demonstrate a long-lasting therapeutic effect on established arthritis of an active immunotherapy to human (h) TNF-alpha and to evaluate the long-term consequences of an endogenous anti-TNF-alpha response.
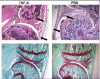
Methods: hTNF-alpha transgenic mice, which spontaneously develop arthritides from 8 weeks of age, were immunized with a heterocomplex (TNF kinoid, or TNF-K) composed of hTNF-alpha and keyhole limpet hemocyanin after disease onset. We evaluated arthritides by clinical and histological assessment, and titers of neutralizing anti-hTNF-alpha antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and L929 assay.
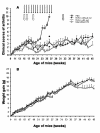
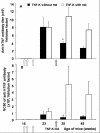
Results: Arthritides were dramatically improved compared to control mice at week 27. TNF-K-treated mice exhibited high levels of neutralizing anti-hTNF-alpha antibodies. Between weeks 27 and 45, all immunized mice exhibited symptoms of clinical deterioration and a parallel decrease in anti-hTNF-alpha neutralizing antibodies. A maintenance dose of TNF-K reversed the clinical deterioration and increased the anti-hTNF-alpha antibody titer. At 45 weeks, TNF-K long-term efficacy was confirmed by low clinical and mild histological scores for the TNF-K-treated mice. Injections of unmodified hTNF-alpha did not induce a recall response to hTNF-alpha in TNF-K immunized mice.
Conclusions: Anti-TNF-alpha immunotherapy with TNF-K has a sustained but reversible therapeutic efficacy in an established disease model, supporting the potential suitability of this approach in treating human disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protection from articular damage by passive or active anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α immunotherapy in human TNF-α transgenic mice depends on anti-TNF-α antibody levels.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Apr;172(1):54-62. doi: 10.1111/cei.12040. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23480185 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) antibody secretion in mice immunized with TNF-α kinoid.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 May;19(5):699-703. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05649-11. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22441388 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of novel bispecific antibody targeting TNF-α/CXCL10 in the treatment of experimental arthritis.Transl Res. 2021 Jun;232:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33453429
-
Strategies for active TNF-α vaccination in rheumatoid arthritis treatment.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 28;31(38):4063-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.06.101. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23845805 Review.
-
The TNF-alpha transgenic mouse model of inflammatory arthritis.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003 Aug;25(1):19-33. doi: 10.1007/s00281-003-0125-3. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003. PMID: 12904889 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunization against an IL-6 peptide induces anti-IL-6 antibodies and modulates the Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity reaction in cynomolgus monkeys.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 19;6:19549. doi: 10.1038/srep19549. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26782790 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic vaccination with TNF-Kinoid in TNF antagonist-resistant rheumatoid arthritis: a phase II randomized, controlled clinical trial.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 17;9(12):e113465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113465. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25517733 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Targeting Can Protect against Arthritis with Low Sensitization to Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 14;8:1533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01533. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29184553 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Costs of TNF-Alpha Blocker Use for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Am Health Drug Benefits. 2013 Mar;6(2):126-36. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2013. PMID: 24991351 Free PMC article.
-
Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR4A2 Is Constitutively Expressed in Cartilage and Upregulated in Inflamed Synovium From hTNF-Alpha Transgenic Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 20;13:835697. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.835697. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35529439 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

