GRASP and IPCEF promote ARF-to-Rac signaling and cell migration by coordinating the association of ARNO/cytohesin 2 with Dock180
- PMID: 20016009
- PMCID: PMC2820421
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-03-0217
GRASP and IPCEF promote ARF-to-Rac signaling and cell migration by coordinating the association of ARNO/cytohesin 2 with Dock180
Abstract
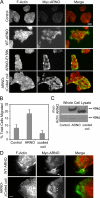
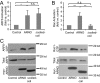
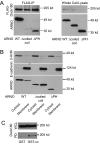
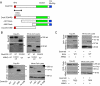
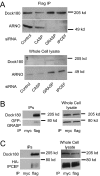
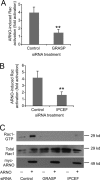
ARFs are small GTPases that regulate vesicular trafficking, cell shape, and movement. ARFs are subject to extensive regulation by a large number of accessory proteins. The many different accessory proteins are likely specialized to regulate ARF signaling during particular processes. ARNO/cytohesin 2 is an ARF-activating protein that promotes cell migration and cell shape changes. We report here that protein-protein interactions mediated by the coiled-coil domain of ARNO are required for ARNO induced motility. ARNO lacking the coiled-coil domain does not promote migration and does not induce ARF-dependent Rac activation. We find that the coiled-coil domain promotes the assembly of a multiprotein complex containing both ARNO and the Rac-activating protein Dock180. Knockdown of either GRASP/Tamalin or IPCEF, two proteins known to bind to the coiled-coil of ARNO, prevents the association of ARNO and Dock180 and prevents ARNO-induced Rac activation. These data suggest that scaffold proteins can regulate ARF dependent processes by biasing ARF signaling toward particular outputs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The scaffolding protein GRASP/Tamalin directly binds to Dock180 as well as to cytohesins facilitating GTPase crosstalk in epithelial cell migration.BMC Cell Biol. 2013 Feb 26;14:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-14-9. BMC Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23441967 Free PMC article.
-
The DOCK180/Elmo complex couples ARNO-mediated Arf6 activation to the downstream activation of Rac1.Curr Biol. 2005 Oct 11;15(19):1749-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.08.052. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16213822
-
ARL4D recruits cytohesin-2/ARNO to modulate actin remodeling.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Nov;18(11):4420-37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0149. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17804820 Free PMC article.
-
Arf GAPs as regulators of the actin cytoskeleton.Biol Cell. 2007 Oct;99(10):583-600. doi: 10.1042/bc20070034. Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17868031 Review.
-
Physiological and Pathological Roles of the Cytohesin Family in Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 3;23(9):5087. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095087. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563476 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Actin Up: An Overview of the Rac GEF Dock1/Dock180 and Its Role in Cytoskeleton Rearrangement.Cells. 2022 Nov 11;11(22):3565. doi: 10.3390/cells11223565. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36428994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-genome methylation analysis of benign and malignant colorectal tumours.J Pathol. 2013 Apr;229(5):697-704. doi: 10.1002/path.4132. Epub 2013 Jan 24. J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23096130 Free PMC article.
-
I'm coming to GEF you: Regulation of RhoGEFs during cell migration.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(6):535-49. doi: 10.4161/cam.28721. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 25482524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand 5F 203 Induces Oxidative Stress That Triggers DNA Damage in Human Breast Cancer Cells.Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):855-71. doi: 10.1021/tx500485v. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25781201 Free PMC article.
-
ARF family G proteins and their regulators: roles in membrane transport, development and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jun;12(6):362-75. doi: 10.1038/nrm3117. Epub 2011 May 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21587297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramoff M. D., Magelhaes P. J., Ram S. J. Image processing with Image. J. Biophotonics Int. 2004;11:36–42.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

