2009 H1N1 influenza
- PMID: 20007905
- PMCID: PMC2800287
- DOI: 10.4065/mcp.2009.0588
2009 H1N1 influenza
Abstract
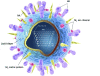
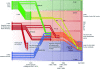
Within 2 months of its discovery last spring, a novel influenza A (H1N1) virus, currently referred to as 2009 H1N1, caused the first influenza pandemic in decades. The virus has caused disproportionate disease among young people with early reports of virulence similar to that of seasonal influenza. This clinical review provides an update encompassing the virology, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of the 2009 H1N1 virus. Because information about this virus, its prevention, and treatment are rapidly evolving, readers are advised to seek additional information. We performed a literature search of PubMed using the following keywords: H1N1, influenza, vaccine, pregnancy, children, treatment, epidemiology, and review. Studies were selected for inclusion in this review on the basis of their relevance. Recent studies and articles were preferred.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Update on 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus.Cleve Clin J Med. 2009 Oct;76(10):577-82. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.76a.05009. Cleve Clin J Med. 2009. PMID: 19797457 Review.
-
Prevention and control of influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2010.MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010 Aug 6;59(RR-8):1-62. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010. PMID: 20689501
-
[The pandemic A/H1N1 in 2009 milder than regular seasonal influenza. Report from Uppsala County].Lakartidningen. 2012 Jun 5-19;109(23-24):1156-8. Lakartidningen. 2012. PMID: 22834207 Swedish. No abstract available.
-
Update on the 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 in children.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010 Feb;22(1):83-7. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e3283350317. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010. PMID: 20068413 Review.
-
Seasonal, avian, and novel H1N1 influenza: prevention and treatment modalities.Ann Pharmacother. 2009 Dec;43(12):2001-11. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M557. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Ann Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19920156 Review.
Cited by
-
Are pigs overestimated as a source of zoonotic influenza viruses?Porcine Health Manag. 2022 Jun 30;8(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40813-022-00274-x. Porcine Health Manag. 2022. PMID: 35773676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes and Risk Factor Analysis of Plastic Bronchitis Among 321 Children with Influenza Pneumonia After Bronchoscopy Examination.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Jun 21;16:4001-4011. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S405444. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37366500 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a bead-based suspension array for the detection of pathogens in acute respiratory tract infections.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 Aug;241(14):1551-8. doi: 10.1177/1535370216647128. Epub 2016 May 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27190247 Free PMC article.
-
Photothermal inactivation of universal viral particles by localized surface plasmon resonance mediated heating filter membrane.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 2;12(1):1724. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05738-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35110635 Free PMC article.
-
Swine-origin influenza a outbreak 2009 at Shinshu University, Japan.BMC Public Health. 2011 Feb 4;11:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-79. BMC Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21291570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Swine influenza A (H1N1) infection in two children—Southern California, March-April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58(15):400-402 - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Update: swine influenza A (H1N1) infections—California and Texas, April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58(16):435-437 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Current WHO phase of pandemic alert. World Health Organization website. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/phase/en/index.html. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/phase/en/index.html Accessed November 10, 2009.
-
- Zimmer SM, Burke DS. Historical perspective—emergence of influenza A (H1N1) viruses. N Engl J Med 2009;361(3):279-285 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

