Genetic analysis of the carboxy-terminal region of the hepatitis C virus core protein
- PMID: 20007277
- PMCID: PMC2812405
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02043-09
Genetic analysis of the carboxy-terminal region of the hepatitis C virus core protein
Abstract
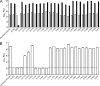
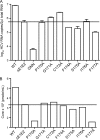
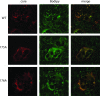
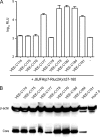
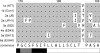
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a liver-tropic pathogen with severe health consequences for infected individuals. Chronic HCV infection can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma and is a leading indicator for liver transplantation. The HCV core protein is an essential component of the infectious virus particle, but many aspects of its role remain undefined. The C-terminal region of the core protein acts as a signal sequence for the E1 glycoprotein and undergoes dual processing events during infectious virus assembly. The exact C terminus of the mature, virion-associated core protein is not known. Here, we performed genetic analyses to map the essential determinants of the HCV core C-terminal region, as well as to define the minimal length of the protein that can function for infectious virus production in trans.
Figures

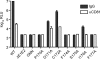
Similar articles
-
Identification of residues in the hepatitis C virus core protein that are critical for capsid assembly in a cell-free system.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(11):6814-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.6814-6826.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15890921 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of hepatitis B virus expression and replication by hepatitis C virus core protein in HuH-7 cells.J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):5823-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.67.10.5823-5832.1993. J Virol. 1993. PMID: 8396658 Free PMC article.
-
Alanine scanning of the hepatitis C virus core protein reveals numerous residues essential for production of infectious virus.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(19):10220-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00793-07. Epub 2007 Jul 18. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17634240 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence variability of HCV Core region: important predictors of HCV induced pathogenesis and viral production.Infect Genet Evol. 2011 Apr;11(3):543-56. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.01.017. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Infect Genet Evol. 2011. PMID: 21292033 Review.
-
Are trans-complementation systems suitable for hepatitis C virus life cycle studies?J Viral Hepat. 2013 Apr;20(4):225-33. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12069. Epub 2013 Feb 14. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23490366 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-translational modifications of hepatitis C viral proteins and their biological significance.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 21;19(47):8929-39. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8929. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24379618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genetic interaction between the core and NS3 proteins of hepatitis C virus is essential for production of infectious virus.J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(23):12351-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05313-11. Epub 2011 Sep 28. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21957313 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional lipid droplet velocities are controlled by differential binding strengths of HCV core DII protein.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 1;8(11):e78065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078065. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223760 Free PMC article.
-
The identification of three sizes of core proteins during the establishment of persistent hepatitis C virus infection in vitro.Virol Sin. 2013 Jun;28(3):129-35. doi: 10.1007/s12250-013-3296-7. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Virol Sin. 2013. PMID: 23543610 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of basic amino acids at the N-terminal end of the core protein that are crucial for hepatitis C virus infectivity.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12515-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01393-10. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20943968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alter, M. J. 2006. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and HIV co-infection. J. Hepatol. 44:S6-S9. - PubMed
-
- Boulant, S., M. W. Douglas, L. Moody, A. Budkowska, P. Targett-Adams, and J. McLauchlan. 2008. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces lipid droplet redistribution in a microtubule- and dynein-dependent manner. Traffic 9:1268-1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

