Therapy of autoinflammatory syndromes
- PMID: 20004774
- PMCID: PMC4508191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.001
Therapy of autoinflammatory syndromes
Abstract
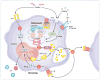
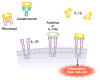
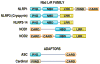
The therapy of autoinflammatory syndromes is an excellent example of the power of translational research. Recent advances in our understanding of the molecular and immunologic basis of this newly identified classification of disease have allowed for the application of novel, effective, targeted treatments with life-changing effects on patients. Although colchicine and TNF-alpha inhibitors are important therapies for specific autoinflammatory syndromes, the novel IL-1-targeted drugs are particularly effective for many of these diseases. Recently, the pharmaceutical industry has adopted a strategy of confirming the efficacy of new targeted drugs in often-ignored patients with orphan diseases, and US Food and Drug Administration policies have allowed for accelerated approval of these drugs, creating a win-win situation for patients and industry. This article reviews the general approach to the therapy of autoinflammatory diseases, focusing on current approved therapies and novel approaches that might be used in the future.
Figures

Comment in
-
Successful canakinumab treatment identifies IL-1β as a pivotal mediator in Schnitzler syndrome.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Dec;128(6):1352-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.05.023. Epub 2011 Jun 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21704363 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Successful canakinumab treatment identifies IL-1β as a pivotal mediator in Schnitzler syndrome.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Dec;128(6):1352-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.05.023. Epub 2011 Jun 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21704363 No abstract available.
-
Dermatologic Manifestations of Monogenic Autoinflammatory Diseases.Dermatol Clin. 2017 Jan;35(1):21-38. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2016.07.005. Dermatol Clin. 2017. PMID: 27890235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The challenge of autoinflammatory syndromes: with an emphasis on hyper-IgD syndrome.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016 Dec;55(suppl 2):ii23-ii29. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew351. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 27856657 Review.
-
Lessons from characterization and treatment of the autoinflammatory syndromes.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017 Mar;29(2):187-194. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000362. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27906774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlling inflammation: contemporary treatments for autoinflammatory diseases and syndromes.Dermatol Clin. 2013 Jul;31(3):507-11. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Dermatol Clin. 2013. PMID: 23827252 Review.
Cited by
-
The NLRP1 inflammasome in skin diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1111611. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1111611. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasome-mediated autoinflammatory disorders.Postgrad Med. 2010 Sep;122(5):125-33. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2010.09.2209. Postgrad Med. 2010. PMID: 20861596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chlamydia-induced reactive arthritis diagnosed during gout flares: A case report and cumulative effect of inflammatory cytokines on chronic arthritis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(40):e17233. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017233. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31577714 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and Regulation of NLRP3 by Sterile and Infectious Insults.Front Immunol. 2022 May 12;13:896353. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.896353. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35663964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome in health and disease: the good, the bad and the ugly.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Oct;166(1):1-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04440.x. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21762124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McDermott MF, Aksentijevich I, Galon J, McDermott EM, Ogunkolade BW, Centola M, et al. Germline mutations in the extracellular domains of the 55 kDa TNF receptor, TNFR1, define a family of dominantly inherited autoinflammatory syndromes. Cell. 1999;97:133–44. - PubMed
-
- McDermott MF, Aksentijevich I. The autoinflammatory syndromes. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;2:511–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

