Loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 function results in adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome
- PMID: 20004762
- PMCID: PMC2790573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.11.010
Loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 function results in adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome
Abstract
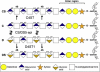
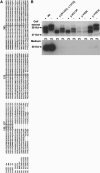
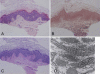
Adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome is an autosomal-recessive disorder characterized by typical facial appearance, wasted build, thin and translucent skin, congenital contractures of thumbs and feet, joint instability, facial clefting, and coagulopathy, as well as heart, kidney, or intestinal defects. We elucidated the molecular basis of the disease by using a SNP array-based genome-wide linkage approach that identified distinct homozygous nonsense and missense mutations in CHST14 in each of four consanguineous families with this disease. The CHST14 gene encodes N-acetylgalactosamine 4-O-sulfotransferase 1 (D4ST1), which catalyzes 4-O sulfation of N-acetylgalactosamine in the repeating iduronic acid-alpha1,3-N-acetylgalactosamine disaccharide sequence to form dermatan sulfate. Mass spectrometry of glycosaminoglycans from a patient's fibroblasts revealed absence of dermatan sulfate and excess of chondroitin sulfate, showing that 4-O sulfation by CHST14 is essential for dermatan sulfate formation in vivo. Our results indicate that adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome is a disorder resulting from a defect specific to dermatan sulfate biosynthesis and emphasize roles for dermatan sulfate in human development and extracellular-matrix maintenance.
Figures

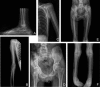

Similar articles
-
Congenital disorders of glycosylation with emphasis on loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2010;93:289-307. doi: 10.1016/S1877-1173(10)93012-3. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2010. PMID: 20807649 Review.
-
Loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 (D4ST1/CHST14) function represents the first dermatan sulfate biosynthesis defect, "dermatan sulfate-deficient adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome".Hum Mutat. 2011 Apr;32(4):484-5. doi: 10.1002/humu.21440. Hum Mutat. 2011. PMID: 21309034 No abstract available.
-
Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (former EDS type VIB) and adducted thumb clubfoot syndrome (ATCS) represent a single clinical entity caused by mutations in the dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 encoding CHST14 gene.Hum Mutat. 2010 Nov;31(11):1233-9. doi: 10.1002/humu.21355. Hum Mutat. 2010. PMID: 20842734
-
A response to: loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 (D4ST1/CHST14) function represents the first dermatan sulfate biosynthesis defect, "dermatan sulfate-deficient Adducted Thumb-Clubfoot Syndrome". Which name is appropriate, "Adducted Thumb-Clubfoot Syndrome" or "Ehlers-Danlos syndrome"?Hum Mutat. 2011 Dec;32(12):1507-9. doi: 10.1002/humu.21586. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Hum Mutat. 2011. PMID: 21964831 No abstract available.
-
CHST14/D4ST1 deficiency: New form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.Pediatr Int. 2016 Feb;58(2):88-99. doi: 10.1111/ped.12878. Pediatr Int. 2016. PMID: 26646600 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological functions of iduronic acid in chondroitin/dermatan sulfate.FEBS J. 2013 May;280(10):2431-46. doi: 10.1111/febs.12214. Epub 2013 Mar 28. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23441919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome with Glycosaminoglycan Abnormalities.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1348:235-249. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-80614-9_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34807422
-
Cardiac Molecular Analysis Reveals Aging-Associated Metabolic Alterations Promoting Glycosaminoglycans Accumulation via Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(38):e2309211. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309211. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39119859 Free PMC article.
-
Defective initiation of glycosaminoglycan synthesis due to B3GALT6 mutations causes a pleiotropic Ehlers-Danlos-syndrome-like connective tissue disorder.Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Jun 6;92(6):935-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.04.016. Epub 2013 May 9. Am J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23664118 Free PMC article.
-
Pingyangmycin inhibits glycosaminoglycan sulphation in both cancer cells and tumour tissues.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Mar;24(6):3419-3430. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15017. Epub 2020 Feb 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32068946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sugahara K., Kitagawa H. Recent advances in the study of the biosynthesis and functions of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000;10:518–527. - PubMed
-
- Evers M.R., Xia G., Kang H.G., Schachner M., Baenziger J.U. Molecular cloning and characterization of a dermatan-specific N-acetylgalactosamine 4-O-sulfotransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:36344–36353. - PubMed
-
- Mikami T., Mizumoto S., Kago N., Kitagawa H., Sugahara K. Specificities of three distinct human chondroitin/dermatan N-acetylgalactosamine 4-O-sulfotransferases demonstrated using partially desulfated dermatan sulfate as an acceptor: Implication of differential roles in dermatan sulfate biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:36115–36127. - PubMed
-
- Hiraoka N., Nakagawa H., Ong E., Akama T.O., Fukuda M.N., Fukuda M. Molecular cloning and expression of two distinct human chondroitin 4-O-sulfotransferases that belong to the HNK-1 sulfotransferase gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:20188–20196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

