Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus is susceptible to AZT
- PMID: 19959199
- PMCID: PMC2821880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.11.013
Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus is susceptible to AZT
Abstract
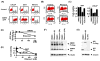
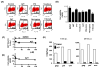
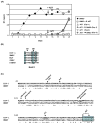
The xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV) is a human retrovirus, recently isolated from tissues of prostate cancer patients with impaired RNase L activity. In this study, we evaluated 10 licensed anti-HIV-1 compounds for their activity against XMRV, including protease inhibitors (PI), nucleoside reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors (NRTI), non-nucleoside RT inhibitors (NNRTI) and an integrase inhibitor. No PI affected XMRV production; even high concentrations of Ritonavir failed to inhibit the maturation of XMRV Gag polyproteins. Among the NRTI, NNRTI and integrase inhibitors used in this study, only AZT blocked XMRV infection and replication through inhibition of viral reverse transcription. This sensitivity of XMRV to AZT may be explained by the modest homology in the motif D sequences of HIV-1 and XMRV reverse transcriptases. If XMRV becomes established as an etiological agent for prostate cancer or other diseases, AZT may be useful for preventing or treating XMRV infections in humans.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biochemical, inhibition and inhibitor resistance studies of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus reverse transcriptase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(1):345-59. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr694. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21908397 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus by APOBEC3 proteins and antiviral drugs.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(11):5719-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00134-10. Epub 2010 Mar 24. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20335265 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of the human retrovirus XMRV to antiretroviral inhibitors.Retrovirology. 2010 Aug 31;7:70. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-7-70. Retrovirology. 2010. PMID: 20807431 Free PMC article.
-
The human retrovirus XMRV in prostate cancer and chronic fatigue syndrome.Nat Rev Urol. 2010 Jul;7(7):392-402. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2010.77. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Nat Rev Urol. 2010. PMID: 20517289 Review.
-
Distribution of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV) infection in chronic fatigue syndrome and prostate cancer.AIDS Rev. 2010 Jul-Sep;12(3):149-52. AIDS Rev. 2010. PMID: 20842203 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilization of replication-competent XMRV reporter-viruses reveals severe viral restriction in primary human cells.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 13;8(9):e74427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074427. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24058563 Free PMC article.
-
The path well traveled: using mammalian retroviruses to guide research on XMRV.Mol Interv. 2010 Feb;10(1):20-4. doi: 10.1124/mi.10.1.5. Mol Interv. 2010. PMID: 20124560 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus in monozygotic twins discordant for chronic fatigue syndrome.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Sep;71(1):66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21795004 Free PMC article.
-
Essential functions of inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) in murine leukemia virus replication.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0115824. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01158-24. Epub 2024 Jun 24. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38912776 Free PMC article.
-
Biology and pathophysiology of the new human retrovirus XMRV and its association with human disease.Immunol Res. 2010 Dec;48(1-3):27-39. doi: 10.1007/s12026-010-8165-y. Immunol Res. 2010. PMID: 20717743
References
-
- Armanios M, Chen JL, Chang YP, Brodsky RA, Hawkins A, Griffin CA, Eshleman JR, Cohen AR, Chakravarti A, Hamosh A, Greider CW. Haploinsufficiency of telomerase reverse transcriptase leads to anticipation in autosomal dominant dyskeratosis congenita. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(44):15960–4. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

