Nuclear isoforms of fibroblast growth factor 2 are novel inducers of hypophosphatemia via modulation of FGF23 and KLOTHO
- PMID: 19933269
- PMCID: PMC2807337
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.030577
Nuclear isoforms of fibroblast growth factor 2 are novel inducers of hypophosphatemia via modulation of FGF23 and KLOTHO
Abstract
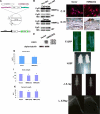
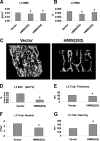
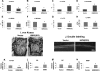
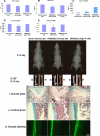
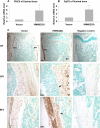
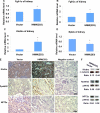
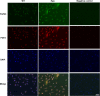
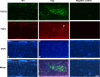
FGF2 transgenic mice were developed in which type I collagen regulatory sequences drive the nuclear high molecular weight FGF2 isoforms in osteoblasts (TgHMW). The phenotype of TgHMW mice included dwarfism, decreased bone mineral density (BMD), osteomalacia, and decreased serum phosphate (P(i)). When TgHMW mice were fed a high P(i) diet, BMD was increased, and dwarfism was partially reversed. The TgHMW phenotype was similar to mice overexpressing FGF23. Serum FGF23 was increased in TgHMW mice. Fgf23 mRNA in bones and fibroblast growth factor receptors 1c and 3c and Klotho mRNAs in kidneys were increased in TgHMW mice, whereas the renal Na(+)/P(i) co-transporter Npt2a mRNA was decreased. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot analyses of TgHMW kidneys showed increased KLOTHO and decreased NPT2a protein. The results suggest that overexpression of HMW FGF2 increases FGF23/FGFR/KLOTHO signaling to down-regulate NPT2a, causing P(i) wasting, osteomalacia, and decreased BMD. We assessed whether HMW FGF2 expression was altered in the Hyp mouse, a mouse homolog of the human disease X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets/osteomalacia. Fgf2 mRNA was increased in bones, and Western blots showed increased FGF2 protein in nuclear fractions from osteoblasts of Hyp mice. In addition, immunohistochemistry demonstrated co-localization of FGF23 and HMW FGF2 protein in osteoblasts and osteocytes from Hyp mice. This study reveals a novel mechanism of regulation of the FGF23-P(i) homeostatic axis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
FGF23 Neutralizing Antibody Ameliorates Hypophosphatemia and Impaired FGF Receptor Signaling in Kidneys of HMWFGF2 Transgenic Mice.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Mar;232(3):610-616. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25458. Epub 2016 Jun 30. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27306296
-
Nuclear fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) isoforms inhibit bone marrow stromal cell mineralization through FGF23/FGFR/MAPK in vitro.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Jan;28(1):35-45. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1721. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 22836867 Free PMC article.
-
FGF23 Neutralizing Antibody Partially Improves Bone Mineralization Defect of HMWFGF2 Isoforms in Transgenic Female Mice.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Jul;33(7):1347-1361. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3417. Epub 2018 Apr 10. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 29502359 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphate transport by fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23): implications for disorders of phosphate metabolism.Pediatr Nephrol. 2010 Apr;25(4):591-601. doi: 10.1007/s00467-009-1273-z. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 19669798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGF23-FGF Receptor/Klotho Pathway as a New Drug Target for Disorders of Bone and Mineral Metabolism.Calcif Tissue Int. 2016 Apr;98(4):334-40. doi: 10.1007/s00223-015-0029-y. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016. PMID: 26126937 Review.
Cited by
-
Skeletal secretion of FGF-23 regulates phosphate and vitamin D metabolism.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Jan 17;8(5):276-86. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.218. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22249518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The kidney sodium-phosphate co-transporter alters bone quality in an age and gender specific manner.Bone. 2013 Apr;53(2):546-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.01.011. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Bone. 2013. PMID: 23333524 Free PMC article.
-
BMP-2 differentially modulates FGF-2 isoform effects in osteoblasts from newborn transgenic mice.Endocrinology. 2013 Aug;154(8):2723-33. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1025. Epub 2013 May 28. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23715864 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of osteocytes in phosphate metabolism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 15;13:967774. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.967774. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35909535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of platelet count, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and platelet/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with serum soluble Klotho.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Aug 17;23(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02242-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39153988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hurley M. M., Marie P. J., Florkiewicz R. Z. (2002) in Principles of Bone Biology (Bilezikian J. P., Raisz L. G., Rodan G. A. eds) pp. 825–851, Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, CA
-
- Muenke M., Schell U. (1995) Trends. Genet. 11, 308–313 - PubMed
-
- De Moerlooze L., Dickson C. (1997) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 7, 378–385 - PubMed
-
- Yu X., White K. E. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 221–232 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

