Cigarette-smoke-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress impairs VEGF- and fluid-shear-stress-mediated signaling in endothelial cells
- PMID: 19929443
- PMCID: PMC2864667
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2009.2874
Cigarette-smoke-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress impairs VEGF- and fluid-shear-stress-mediated signaling in endothelial cells
Retraction in
-
Retraction: cigarette smoke-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress impairs VEGF- and fluid shear stress-mediated signaling in endothelial cells. Edirisinghe I, Arunachalam G, Wong C, Yao H, Rahman A, Phipps RP, Jin ZG, and Rahman I. Antioxid Redox Signal 12: 1355-1369, 2010.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Apr 20;18(12):1535. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.5170. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23259579 Free PMC article.
Abstract
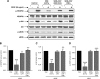
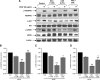
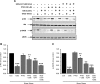
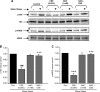
VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2), a tyrosine kinase receptor, is activated by VEGF and fluid shear stress (FSS), and its downstream signaling is important in the regulation of endothelial functions, such as cell migration, endothelium-dependent relaxation, and angiogenesis. Cigarette smoke (CS) is known to cause oxidative/nitrosative stress, leading to modifications of tyrosine kinase receptors and impaired downstream signaling. We hypothesized that CS-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress impairs VEGF- and FSS-mediated VEGFR2 activation, leading to endothelial dysfunction. Human lung microvascular endothelial cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells were treated with different concentrations of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) to investigate the VEGF- or FSS-mediated VEGFR2 phosphorylation and its downstream signaling involved in endothelial function. CSE treatment impaired both VEGF- and FSS-mediated VEGFR2 phosphorylation, resulting in impaired endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation by Akt. CS-derived reactive oxygen/nitrogen species react with VEGFR2, rendering VEGFR2 inactive for its downstream signaling. Pretreatment with nitric oxide scavenger (PTIO), reactive oxygen species scavengers (combination of SOD with catalase), and N-acetyl-L-cysteine, significantly attenuated the CSE-induced impairment of VEGF-mediated Akt and eNOS phosphorylation. These findings suggest that CSE-induced oxidative/nitrosative stress impairs VEGF- and FSS-mediated endothelial cell function and has important implications in the pathogenesis of CS-induced pulmonary and cardiovascular diseases associated with endothelial dysfunction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cigarette smoke-mediated oxidative stress, shear stress, and endothelial dysfunction: role of VEGFR2.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Aug;1203:66-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05601.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20716285 Review.
-
Cigarette smoke exposure impairs VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration: role of NO and reactive oxygen species.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006 Aug;41(2):275-84. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.05.004. Epub 2006 Jun 27. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16806264
-
IQGAP1, a novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding protein, is involved in reactive oxygen species--dependent endothelial migration and proliferation.Circ Res. 2004 Aug 6;95(3):276-83. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000136522.58649.60. Epub 2004 Jun 24. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15217908
-
An ezrin/calpain/PI3K/AMPK/eNOSs1179 signaling cascade mediating VEGF-dependent endothelial nitric oxide production.Circ Res. 2009 Jan 2;104(1):50-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.178467. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19038867 Free PMC article.
-
Shear-induced endothelial mechanotransduction: the interplay between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) and the pathophysiological implications.J Biomed Sci. 2014 Jan 13;21(1):3. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-21-3. J Biomed Sci. 2014. PMID: 24410814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis and necrosis: two different outcomes of cigarette smoke condensate-induced endothelial cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Nov 15;3(11):e424. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.162. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 23152060 Free PMC article.
-
COPD/emphysema: The vascular story.Pulm Circ. 2011 Jul-Sep;1(3):320-6. doi: 10.4103/2045-8932.87295. Pulm Circ. 2011. PMID: 22140621 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 regulates oxidant- and cigarette smoke-induced eNOS acetylation in endothelial cells: Role of resveratrol.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Feb 26;393(1):66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.080. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20102704 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of lung endothelial barrier disruption induced by cigarette smoke: role of oxidative stress and ceramides.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):L836-46. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00385.2010. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21873444 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel In Vivo Model to Study Impaired Tissue Regeneration Mediated by Cigarette Smoke.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 19;8(1):10926. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28687-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30026555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrose JA. Barua RS. The pathophysiology of cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:1731–1737. - PubMed
-
- Bagi Z. Cseko C. Toth E. Koller A. Oxidative stress-induced dysregulation of arteriolar wall shear stress and blood pressure in hyperhomocysteinemia is prevented by chronic vitamin C treatment. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285:H2277–2283. - PubMed
-
- Barbera JA. Peinado VI. Santos S. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2003;21:892–905. - PubMed
-
- Berk BC. Atheroprotective signaling mechanisms activated by steady laminar flow in endothelial cells. Circulation. 2008;117:1082–1089. - PubMed
-
- Boo YC. Hwang J. Sykes M. Michell BJ. Kemp BE. Lum H. Jo H. Shear stress stimulates phosphorylation of eNOS at Ser(635) by a protein kinase A-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283:H1819–H1828. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

