Anthrax lethal toxin induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cytosolic cathepsin release is Nlrp1b/Nalp1b-dependent
- PMID: 19924255
- PMCID: PMC2775945
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007913
Anthrax lethal toxin induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cytosolic cathepsin release is Nlrp1b/Nalp1b-dependent
Abstract
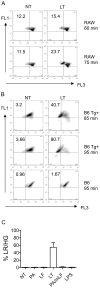
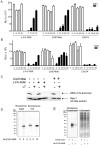
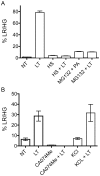
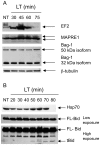
NOD-like receptors (NLRs) are a group of cytoplasmic molecules that recognize microbial invasion or 'danger signals'. Activation of NLRs can induce rapid caspase-1 dependent cell death termed pyroptosis, or a caspase-1 independent cell death termed pyronecrosis. Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin (LT), is recognized by a subset of alleles of the NLR protein Nlrp1b, resulting in pyroptotic cell death of macrophages and dendritic cells. Here we show that LT induces lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP). The presentation of LMP requires expression of an LT-responsive allele of Nlrp1b, and is blocked by proteasome inhibitors and heat shock, both of which prevent LT-mediated pyroptosis. Further the lysosomal protease cathepsin B is released into the cell cytosol and cathepsin inhibitors block LT-mediated cell death. These data reveal a role for lysosomal membrane permeabilization in the cellular response to bacterial pathogens and demonstrate a shared requirement for cytosolic relocalization of cathepsins in pyroptosis and pyronecrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anthrax and the inflammasome.Microbes Infect. 2012 May;14(5):392-400. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.12.005. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22207185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CA-074Me protection against anthrax lethal toxin.Infect Immun. 2009 Oct;77(10):4327-36. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00730-09. Epub 2009 Jul 27. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19635822 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax lethal toxin activates the inflammasome in sensitive rat macrophages.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Aug 6;398(4):785-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.039. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20638366 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting edge: resistance to Bacillus anthracis infection mediated by a lethal toxin sensitive allele of Nalp1b/Nlrp1b.J Immunol. 2010 Jan 1;184(1):17-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903114. Epub 2009 Nov 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19949100 Free PMC article.
-
[Lysosomal membrane permeabilization as apoptogenic factor].Tsitologiia. 2011;53(4):313-24. Tsitologiia. 2011. PMID: 21675210 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The endolysosomal system in cell death and survival.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Jan 1;5(1):a008755. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008755. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23284043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthrax and the inflammasome.Microbes Infect. 2012 May;14(5):392-400. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.12.005. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22207185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Outcome of the Cryptococcus neoformans-Macrophage Interaction Depends on Phagolysosomal Membrane Integrity.J Immunol. 2018 Jul 15;201(2):583-603. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700958. Epub 2018 Jun 1. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29858266 Free PMC article.
-
Auranofin protects against anthrax lethal toxin-induced activation of the Nlrp1b inflammasome.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Mar;55(3):1028-35. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00772-10. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21149629 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax Toxins in Context of Bacillus anthracis Spores and Spore Germination.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Aug 17;7(8):3167-78. doi: 10.3390/toxins7083167. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26287244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McIntire CR, Yeretssian G, Saleh M. Inflammasomes in infection and inflammation. Apoptosis 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

