N-linked glycosylation is essential for the stability but not the signaling function of the interleukin-6 signal transducer glycoprotein 130
- PMID: 19915009
- PMCID: PMC2804336
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.075952
N-linked glycosylation is essential for the stability but not the signaling function of the interleukin-6 signal transducer glycoprotein 130
Abstract
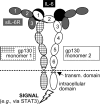
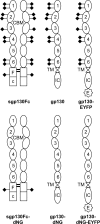
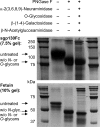
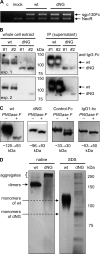
N-Linked glycosylation is an important determinant of protein structure and function. The interleukin-6 signal transducer glycoprotein 130 (gp130) is a common co-receptor for cytokines of the interleukin (IL)-6 family and is N-glycosylated at 9 of 11 potential sites. Whereas N-glycosylation of the extracellular domains D1-D3 of gp130 has been shown to be dispensable for binding of the gp130 ligand IL-6 and its cognate receptor in vitro, the role of the N-linked glycans on domains D4 and D6 is still unclear. We have mutated the asparagines of all nine functional N-glycosylation sites of gp130 to glutamine and systematically analyzed the consequences of deleted N-glycosylation (dNG) in both cellular gp130 and in a soluble gp130-IgG1-Fc fusion protein (sgp130Fc). Our results show that sgp130Fc-dNG is inherently unstable and degrades rapidly under conditions that do not harm wild-type sgp130Fc. Consistently, the bulk of cellular gp130-dNG is not transported to the plasma membrane but is degraded in the proteasome. However, the small quantities of gp130-dNG, which do reach the cell surface, are still able to activate the key gp130 signaling target signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) upon binding of the agonistic complex of IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptor. In conclusion, N-linked glycosylation is required for the stability but not the signal-transducing function of gp130.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structure of the unliganded extracellular domain of the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130 in solution.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Jun-Jul;90(6-7):515-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.09.012. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21035897
-
Importance of the membrane-proximal extracellular domains for activation of the signal transducer glycoprotein 130.J Immunol. 2000 Jan 1;164(1):273-82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.1.273. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10605021
-
Dynamics of the gp130 cytokine complex: a model for assembly on the cellular membrane.Protein Sci. 2005 Mar;14(3):783-90. doi: 10.1110/ps.041117105. Protein Sci. 2005. PMID: 15722452 Free PMC article.
-
Functional properties of extracellular domains of transducer receptor gp130.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011 Apr;76(4):394-406. doi: 10.1134/s000629791104002x. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011. PMID: 21585315 Review.
-
Survival pathways in hypertrophy and heart failure: the gp130-STAT3 axis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2007 Jul;102(4):279-97. doi: 10.1007/s00395-007-0658-z. Epub 2007 May 29. Basic Res Cardiol. 2007. Corrected and republished in: Basic Res Cardiol. 2007 Sep;102(5):393-411. doi: 10.1007/s00395-007-0674-z PMID: 17530315 Corrected and republished. Review.
Cited by
-
Dominant-negative mutations in human IL6ST underlie hyper-IgE syndrome.J Exp Med. 2020 Jun 1;217(6):e20191804. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191804. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32207811 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a new variation in DPM2 gene in two Chinese siblings with mild intellectual impairment.Front Genet. 2023 Apr 19;14:930692. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.930692. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37152991 Free PMC article.
-
oHSV-P10 reduces glioma stem cell enrichment after oncolytic HSV therapy.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023 Apr 3;29:30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.03.003. eCollection 2023 Jun 15. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023. PMID: 37114074 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Effects of Deuterium-Depleted Water on the Expression of GLUT4 and Insulin Resistance in the Muscle Cell Line C2C12.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):1771. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081771. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200235 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β sensitivity is determined by N-linked glycosylation of the type II TGF-β receptor.Biochem J. 2012 Aug 1;445(3):403-11. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111923. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22571197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitra N., Sinha S., Ramya T. N., Surolia A. (2006) Trends Biochem. Sci. 31, 156–163 - PubMed
-
- Slieker L. J., Lane M. D. (1985) J. Biol. Chem. 260, 687–690 - PubMed
-
- Ding D. X., Vera J. C., Heaney M. L., Golde D. W. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, 24580–24584 - PubMed
-
- Zhou H., Tai H. H. (1999) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 369, 267–276 - PubMed
-
- Wenzel-Seifert K., Seifert R. (2003) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 301, 693–698 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

