SNX-BAR proteins in phosphoinositide-mediated, tubular-based endosomal sorting
- PMID: 19914387
- PMCID: PMC4052211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.11.009
SNX-BAR proteins in phosphoinositide-mediated, tubular-based endosomal sorting
Abstract
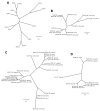
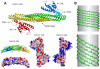
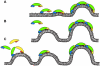
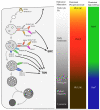
The endocytic network is morphologically characterized by a wide variety of membrane bound compartments that are able to undergo dynamic re-modeling through tubular and vesicular structures. The precise molecular mechanisms governing such re-modeling, and the events that co-ordinated this with the major role of endosomes, cargo sorting, remain unclear. That said, recent work on a protein family of sorting nexins (SNX) - especially a subfamily of SNX that contain a BAR domain (SNX-BARs) - has begun to shed some much needed light on these issues and in particular the process of tubular-based endosomal sorting. SNX-BARs are evolutionary conserved in endosomal protein complexes such as retromer, where they co-ordinate membrane deformation with cargo selection. Furthermore a central theme emerges of SNX-BARs linking the forming membrane carrier to cytoskeletal elements for transport through motor proteins such as dynein. By studying these SNX-BARs, we are gaining an increasingly detailed appreciation of the mechanistic basis of endosomal sorting and how this highly dynamic process functions in health and disease.
(c) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The retromer coat complex coordinates endosomal sorting and dynein-mediated transport, with carrier recognition by the trans-Golgi network.Dev Cell. 2009 Jul;17(1):110-22. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.04.016. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19619496 Free PMC article.
-
SNX-3 mediates retromer-independent tubular endosomal recycling by opposing EEA-1-facilitated trafficking.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jun 3;17(6):e1009607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009607. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34081703 Free PMC article.
-
The VINE complex is an endosomal VPS9-domain GEF and SNX-BAR coat.Elife. 2022 Aug 8;11:e77035. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77035. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35938928 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal sorting and signalling: an emerging role for sorting nexins.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jul;9(7):574-82. doi: 10.1038/nrm2427. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18523436 Review.
-
Retromer and sorting nexins in endosomal sorting.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Feb;43(1):33-47. doi: 10.1042/BST20140290. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 25619244 Review.
Cited by
-
VPS35 regulates developing mouse hippocampal neuronal morphogenesis by promoting retrograde trafficking of BACE1.Biol Open. 2012 Dec 15;1(12):1248-57. doi: 10.1242/bio.20122451. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Biol Open. 2012. PMID: 23259059 Free PMC article.
-
Let's go bananas: revisiting the endocytic BAR code.EMBO J. 2011 Aug 31;30(17):3501-15. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.266. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21878992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamin-Independent Mechanisms of Endocytosis and Receptor Trafficking.Cells. 2022 Aug 17;11(16):2557. doi: 10.3390/cells11162557. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trafficking of Vacuolar Sorting Receptors: New Data and New Problems.Plant Physiol. 2014 Aug;165(4):1417-1423. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.243303. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24951487 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans as a model for membrane traffic.WormBook. 2014 Apr 25:1-47. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.77.2. WormBook. 2014. PMID: 24778088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sakamuro D, Elliott KJ, Wechsler-Reya R, Prendergast GC. BIN1 is a novel MYC-interacting protein with features of a tumour suppressor. Nat Genet. 1996;14:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Peter BJ, Kent HM, Mills IG, Vallis Y, Butler PJ, Evans PR, McMahon HT. BAR domains as sensors of membrane curvature: the amphiphysin BAR structure. Science. 2004;303:495–9. - PubMed
-
- McMahon HT, Gallop JL. Membrane curvature and mechanisms of dynamic cell membrane remodelling. Nature. 2005;438:590–6. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerberg J, McLaughlin S. Membrane curvature: how BAR domains bend bilayers. Curr Biol. 2004;14:R250–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

