Clinical factors associated with dense and wedge-shaped nephrograms detected 24 h after chemoembolization
- PMID: 19911454
- PMCID: PMC2773365
- DOI: 10.1007/s00270-009-9692-6
Clinical factors associated with dense and wedge-shaped nephrograms detected 24 h after chemoembolization
Abstract
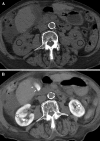
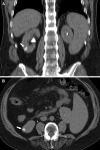
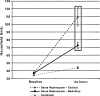
This investigation aimed to evaluate patient characteristics and procedural factors associated with abnormal nephrograms encountered on noncontrast computed axial tomography (CAT) obtained 24-h after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies. Sixty hepatic chemoembolization procedures were performed in 29 patients who had a median age of 63 years (range 42-79). The male-to-female ratio was 16:13. Noncontrast CAT scans were obtained approximately 24 h after TACE as part of our institutional protocol and were examined for persistent renal nephrograms. These findings were compared with clinical and procedural parameters to determine whether there was any association with these factors or with the occurrence of acute renal failure (ARF). Abnormally persistent CAT nephrograms were observed 24 h after 28 of 60 (46.7%) TACE procedures, of which 14 (23.3%) were persistent, bilaterally dense, global nephrograms, and 14 (23.3%) were small, wedge-shaped, and focal nephrograms. The change in serum creatinine from baseline to 24 h was significantly greater (p=0.031) in the global nephrogram group. The presence of cirrhosis, Child-Pugh score, procedure time, baseline renal insufficiency, and lower periprocedural mean arterial blood pressure were also statistically significantly associated with the occurrence of bilateral globally dense nephrograms. The procedure time was statistically significantly associated with the occurrence of wedge-like focally persistent nephrograms. Global, persistently dense nephrograms and wedge-shaped focally persistent nephrograms are not infrequently observed after TACE. Persistent global nephrograms can be an important clinical indicator of ARF. The wedge nephrogram may represent focal renal ischemia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bilateral Sustained Nephrograms After Parenteral Administration of Iodinated Contrast Material: A Potential Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury, Dialysis, and Mortality.Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 Jul;93(7):867-876. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.02.023. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018. PMID: 29976375
-
Clinical Significance of Persistent Global and Focal Computed Tomography Nephrograms After Cardiac Catheterization and Their Relationships to Urinary Biomarkers of Kidney Damage and Procedural Factors: Pilot Study.Invest Radiol. 2016 Dec;51(12):797-803. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000268. Invest Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26974312
-
[Incidence and risk factors of acute renal failure after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma].Korean J Hepatol. 2008 Jun;14(2):168-77. doi: 10.3350/kjhep.2008.14.2.168. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18617764 Korean.
-
[Transarterial chemoembolization of liver metastases of colorectal carcinoma using degradable starch microspheres (Spherex): personal investigations and review of the literature].Radiologe. 2005 Jul;45(7):633-43. doi: 10.1007/s00117-004-1061-5. Radiologe. 2005. PMID: 15316615 Review. German.
-
Optimizing the treatment of liver metastases from uveal melanomas with transarterial chemoembolization using melphalan and calibrated microspheres.Bull Cancer. 2020 Dec;107(12):1274-1283. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2020.09.010. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Bull Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33183739 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic factors for acute kidney injury following transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Apr 15;7(5):2579-86. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24966972 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent CT nephrograms following cardiac catheterisation and intervention: initial observations.Insights Imaging. 2012 Feb;3(1):49-60. doi: 10.1007/s13244-011-0131-2. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Insights Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22695998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Older RA, Miller JP, Jackson DC, et al. Angiographically induced renal failure and its radiographic detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976;126:1039–1045. - PubMed
-
- Older RA, Korobkin M, Cleeve DM, et al. Contrast-induced acute renal failure: persistent nephrogram as clue to early detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980;134:339–342. - PubMed
-
- Love L, Lind JA, Olson MC. Persistent CT nephrogram with significance in the diagnosis of contrast nephropathy. Radiology. 1989;172:125–129. - PubMed

