Structure of the zinc-bound amino-terminal domain of the NMDA receptor NR2B subunit
- PMID: 19910922
- PMCID: PMC2797058
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.338
Structure of the zinc-bound amino-terminal domain of the NMDA receptor NR2B subunit
Abstract
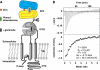
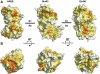
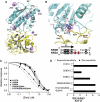
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors belong to the family of ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) that mediate the majority of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the mammalian brain. One of the hallmarks for the function of NMDA receptors is that their ion channel activity is allosterically regulated by binding of modulator compounds to the extracellular amino-terminal domain (ATD) distinct from the L-glutamate-binding domain. The molecular basis for the ATD-mediated allosteric regulation has been enigmatic because of a complete lack of structural information on NMDA receptor ATDs. Here, we report the crystal structures of ATD from the NR2B NMDA receptor subunit in the zinc-free and zinc-bound states. The structures reveal the overall clamshell-like architecture distinct from the non-NMDA receptor ATDs and molecular determinants for the zinc-binding site, ion-binding sites, and the architecture of the putative phenylethanolamine-binding site.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


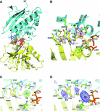
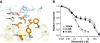
Similar articles
-
Subunit arrangement and phenylethanolamine binding in GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors.Nature. 2011 Jun 15;475(7355):249-53. doi: 10.1038/nature10180. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21677647 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a heterotetrameric NMDA receptor ion channel.Science. 2014 May 30;344(6187):992-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1251915. Science. 2014. PMID: 24876489 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of agonist efficacy at the glutamate binding site of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.Mol Pharmacol. 2013 Jul;84(1):114-27. doi: 10.1124/mol.113.085803. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Mol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23625947 Free PMC article.
-
Amino terminal domain regulation of NMDA receptor function.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 1;500(1-3):101-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.015. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15464024 Review.
-
Structure, Dynamics, and Allosteric Potential of Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor N-Terminal Domains.Biophys J. 2015 Sep 15;109(6):1136-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.061. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26255587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of the glutamate receptor GluA1 N-terminal domain.Biochem J. 2011 Sep 1;438(2):255-63. doi: 10.1042/BJ20110801. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21639859 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the study of anesthesia-and analgesia-related mechanisms of S-ketamine.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 14;14:1228895. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1228895. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37781698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Separation of domain contacts is required for heterotetrameric assembly of functional NMDA receptors.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 9;31(10):3565-79. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6041-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21389213 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of positive allosteric modulation of GluN2B NMDA receptors by polyamines.EMBO J. 2011 Jun 17;30(15):3134-46. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.203. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21685875 Free PMC article.
-
Amino terminal domains of the NMDA receptor are organized as local heterodimers.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 22;6(4):e19180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019180. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21544205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC (2002) PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58: 1948–1954 - PubMed
-
- Alarcon K, Martz A, Mony L, Neyton J, Paoletti P, Goeldner M, Foucaud B (2008) Reactive derivatives for affinity labeling in the ifenprodil site of NMDA receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 2765–2770 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Gouaux E (2000) Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron 28: 165–181 - PubMed
-
- Choi YB, Lipton SA (1999) Identification and mechanism of action of two histidine residues underlying high-affinity Zn2+ inhibition of the NMDA receptor. Neuron 23: 171–180 - PubMed
-
- Clayton A, Siebold C, Gilbert RJ, Sutton GC, Harlos K, McIlhinney RA, Jones EY, Aricescu AR (2009) Crystal structure of the GluR2 amino-terminal domain provides insights into the architecture and assembly of ionotropic glutamate receptors. J Mol Biol 392: 1125–1132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

