PKCtheta is required for alloreactivity and GVHD but not for immune responses toward leukemia and infection in mice
- PMID: 19907075
- PMCID: PMC2786796
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI39692
PKCtheta is required for alloreactivity and GVHD but not for immune responses toward leukemia and infection in mice
Abstract
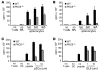
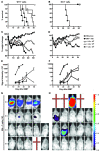
When used as therapy for hematopoietic malignancies, allogeneic BM transplantation (BMT) relies on the graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect to eradicate residual tumor cells through immunologic mechanisms. However, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), which is initiated by alloreactive donor T cells that recognize mismatched major and/or minor histocompatibility antigens and cause severe damage to hematopoietic and epithelial tissues, is a potentially lethal complication of allogeneic BMT. To enhance the therapeutic potential of BMT, we sought to find therapeutic targets that could inhibit GVHD while preserving GVL and immune responses to infectious agents. We show here that T cell responses triggered in mice by either Listeria monocytogenes or administration of antigen and adjuvant were relatively well preserved in the absence of PKC isoform theta (PKCtheta), a key regulator of TCR signaling. In contrast, PKCtheta was required for alloreactivity and GVHD induction. Furthermore, absence of PKCtheta raised the threshold for T cell activation, which selectively affected alloresponses. Most importantly, PKCtheta-deficient T cells retained the ability to respond to virus infection and to induce GVL effect after BMT. These findings suggest PKCtheta is a potentially unique therapeutic target required for GVHD induction but not for GVL or protective responses to infectious agents.
Figures
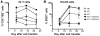
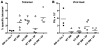
Similar articles
-
Pharmacologic inhibition of PKCα and PKCθ prevents GVHD while preserving GVL activity in mice.Blood. 2013 Oct 3;122(14):2500-11. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-12-471938. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23908466 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-17-92 controls T-cell responses in graft-versus-host disease and leukemia relapse in mice.Blood. 2015 Sep 10;126(11):1314-23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-627356. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26138686 Free PMC article.
-
IL-11 separates graft-versus-leukemia effects from graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation.J Clin Invest. 1999 Aug;104(3):317-25. doi: 10.1172/JCI7111. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10430613 Free PMC article.
-
Alloreactivity and the predictive value of anti-recipient specific interleukin 2 producing helper T lymphocyte precursor frequencies for alloreactivity after bone marrow transplantation.Dan Med Bull. 2002 May;49(2):89-108. Dan Med Bull. 2002. PMID: 12064093 Review.
-
Th2 and Tc2 cells in the regulation of GVHD, GVL, and graft rejection: considerations for the allogeneic transplantation therapy of leukemia and lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000 Jul;38(3-4):221-34. doi: 10.3109/10428190009087014. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000. PMID: 10830730 Review.
Cited by
-
A MLR-Based Approach to Analyze Regulators of T Lymphocyte Activation In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 10;23(10):5337. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105337. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628145 Free PMC article.
-
DOT1L inhibition attenuates graft-versus-host disease by allogeneic T cells in adoptive immunotherapy models.Nat Commun. 2018 May 15;9(1):1915. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04262-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29765028 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel PKCθ from Benchtop to Clinic.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:348798. doi: 10.1155/2015/348798. Epub 2015 May 19. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26090489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antigen-presenting cell-derived complement modulates graft-versus-host disease.J Clin Invest. 2012 Jun;122(6):2234-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI61019. Epub 2012 May 15. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22585573 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB is crucial in proximal T-cell signaling for calcium influx and NFAT activation.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Dec;44(12):3741-6. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444904. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25251667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Curtsinger J.M., Gerner M.Y., Lins D.C., Mescher M.F. Signal 3 availability limits the CD8 T cell response to a solid tumor. J. Immunol. 2007;178:6752–6760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

