Side chain specificity of ADP-ribosylation by a sirtuin
- PMID: 19895577
- PMCID: PMC2805772
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07427.x
Side chain specificity of ADP-ribosylation by a sirtuin
Abstract
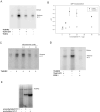
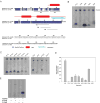
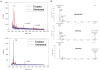
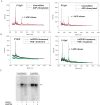
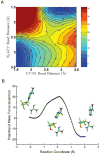
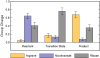
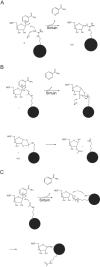
Endogenous mono-ADP-ribosylation in eukaryotes is involved in regulating protein synthesis, signal transduction, cytoskeletal integrity, and cell proliferation, although few cellular ADP-ribosyltransferases have been identified. The sirtuins constitute a highly conserved family of protein deacetylases, and several family members have also been reported to perform protein ADP-ribosylation. We characterized the ADP-ribosylation reaction of the nuclear sirtuin homolog Trypanosoma brucei SIR2-related protein 1 (TbSIR2RP1) on both acetylated and unacetylated substrates. We demonstrated that an acetylated substrate is not required for ADP-ribosylation to occur, indicating that the reaction performed by TbSIR2RP1 is a genuine enzymatic reaction and not a side reaction of deacetylation. Biochemical and MS data showed that arginine is the major ADP-ribose acceptor for unacetylated substrates, whereas arginine does not appear to be the major ADP-ribose acceptor in reactions with acetylated histone H1.1. We performed combined ab initio quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical molecular dynamics simulations, which indicated that sirtuin ADP-ribosylation at arginine is energetically feasible, and involves a concerted mechanism with a highly dissociative transition state. In comparison with the corresponding nicotinamide cleavage in the deacetylation reaction, the simulations suggest that sirtuin ADP-ribosylation would be several orders slower but less sensitive to nicotinamide inhibition, which is consistent with experimental results. These results suggest that TbSIR2RP1 can perform ADP-ribosylation using two distinct mechanisms, depending on whether or not the substrate is acetylated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acetylation-dependent ADP-ribosylation by Trypanosoma brucei Sir2.J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 29;283(9):5317-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707613200. Epub 2007 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18165239
-
Structure-based mechanism of ADP-ribosylation by sirtuins.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 27;284(48):33654-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.024521. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19801667 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of sirtuins with NAD analogues and 32P-NAD.Biochemistry. 2009 Apr 7;48(13):2878-90. doi: 10.1021/bi802093g. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19220062
-
ADP-Ribosylation, a Multifaceted Posttranslational Modification Involved in the Control of Cell Physiology in Health and Disease.Chem Rev. 2018 Feb 14;118(3):1092-1136. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00122. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29172462 Review.
-
Sirtuin chemical mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1804(8):1591-603. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.01.021. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20132909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a Class of Protein ADP-Ribosylating Sirtuins in Microbial Pathogens.Mol Cell. 2015 Jul 16;59(2):309-20. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26166706 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering enzyme function using peptide arrays.Mol Biotechnol. 2011 Nov;49(3):283-305. doi: 10.1007/s12033-011-9402-x. Mol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21604200 Review.
-
SirT7 auto-ADP-ribosylation regulates glucose starvation response through mH2A1.Sci Adv. 2020 Jul 24;6(30):eaaz2590. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz2590. eCollection 2020 Jul. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32832656 Free PMC article.
-
Time-of-flights and traps: from the Histone Code to Mars.Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2010;16(3):331-40. doi: 10.1255/ejms.1082. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2010. PMID: 20530839 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 3: physiological modulators of metabolism.Physiol Rev. 2012 Jul;92(3):1479-514. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00022.2011. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22811431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sommer N, Salniene V, Gineikiene E, Nivinskas R, Ruger W. T4 early promoter strength probed in vivo with unribosylated and ADP-ribosylated Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a mutation analysis. Microbiology. 2000;146:2643–2653. - PubMed
-
- Sekine A, Fujiwara M, Narumiya S. Asparagine residue in the rho gene product is the modification site for botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1989;264:8602–8605. - PubMed
-
- Parikh SL, Schramm VL. Transition State Structure for ADP-Ribosylation of Eukaryotic Elongation Factor 2 Catalyzed by Diphtheria Toxin. Biochemistry. 2004;43:1204–1212. - PubMed
-
- Vecchio MD, Balducci E. Mono ADP-ribosylation inhibitors prevent inflammatory cytokine release in alveolar epithelial cells. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2008;310:77–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

