Effect of killer immunoglobulin-like receptors in the response to combined treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection
- PMID: 19846535
- PMCID: PMC2798445
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01285-09
Effect of killer immunoglobulin-like receptors in the response to combined treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection
Abstract
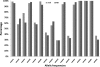
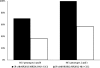
Killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are related to the activation and inhibition of NK cells and may play an important role in the innate response against infection with viruses such as hepatitis C virus (HCV). We examined whether the different combinations of KIRs with their HLA class I ligands influenced the response to combined treatment (pegylated alpha interferon and ribavirin) of patients infected by HCV. A total of 186 consecutive patients diagnosed with chronic HCV infection were analyzed. Seventy-seven patients exhibited HCV RNA levels at 6 months posttreatment and were called nonresponders (NR), while 109 cleared viral RNA and were named sustained viral responders (SVR). Patients were typed for HLA-B, HLA-Cw, KIR genes, and HCV genotype. In our study, the frequency of the KIR2DL2 allele was significantly increased in NR (P < 0.001; odds ratio [OR] = 1.95), as was the frequency of the KIR2DL2/KIR2DL2 genotype (P < 0.005; OR = 2.52). In contrast, the frequencies of the KIR2DL3 genotype (P < 0.001) and KIR2DL3/KIR2DL3 genotype (P < 0.05; OR = 0.54) were significantly increased in the SVR. Different combinations of KIR2DL2 and KIR2DL3 alleles with their ligands were analyzed. The frequency of the KIR2DL2/KIR2DL2-HLA-C1C2 genotype was significantly increased in the NR (P < 0.01; OR = 3.15). Additionally, we found a higher frequency of the KIR2DL3/KIR2DL3-HLA-C1C1 genotype in the SVR group (P < 0.05; OR = 0.33). These results were not affected by the HCV genotype. In conclusion, patients who carried the KIR2DL2/KIR2DL2-HLA-C1C2 genotype were less prone to respond to treatment. However, the KIR2DL3/KIR2DL3-HLA-C1C1 genotype clearly correlated with a satisfactory response to treatment, defined by the clearance of HCV RNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL28B, HLA-C, and KIR variants additively predict response to therapy in chronic hepatitis C virus infection in a European Cohort: a cross-sectional study.PLoS Med. 2011 Sep;8(9):e1001092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001092. Epub 2011 Sep 13. PLoS Med. 2011. PMID: 21931540 Free PMC article.
-
KIR, HLA, and IL28B variant predict response to antiviral therapy in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C patients in Japan.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 12;8(12):e83381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083381. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349500 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diversity of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genotypes and KIR2DL2/3 variants in HCV treatment outcome.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 13;9(6):e99426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099426. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24927414 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS2 (KIR2DS2) and KIR2DL2 is associated with poor responses to therapy of recurrent hepatitis C virus in liver transplant recipients.Liver Transpl. 2009 Nov;15(11):1557-63. doi: 10.1002/lt.21878. Liver Transpl. 2009. PMID: 19877200
-
Association of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors with spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus in the Chinese population.Transfusion. 2018 Apr;58(4):1028-1035. doi: 10.1111/trf.14527. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Transfusion. 2018. PMID: 29446443
Cited by
-
IL-12 and IL-15 induce the expression of CXCR6 and CD49a on peripheral natural killer cells.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2018 Mar;6(1):34-46. doi: 10.1002/iid3.190. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2018. PMID: 28952190 Free PMC article.
-
Inherent transcriptional signatures of NK cells are associated with response to IFNα + rivabirin therapy in patients with Hepatitis C Virus.J Transl Med. 2015 Mar 1;13:77. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0428-x. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25849716 Free PMC article.
-
The New Kid on the Block: HLA-C, a Key Regulator of Natural Killer Cells in Viral Immunity.Cells. 2021 Nov 10;10(11):3108. doi: 10.3390/cells10113108. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term effect on natural killer cells by interferon-α therapy on the outcomes of HCV infection.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014 May;34(5):366-75. doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0049. Epub 2013 Dec 24. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014. PMID: 24367931 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Natural cytotoxicity receptor-dependent natural killer cytolytic activity directed at hepatitis C Virus (HCV) is associated with liver inflammation, African American race, IL28B genotype, and response to pegylated interferon/ribavirin therapy in chronic HCV infection.J Infect Dis. 2014 May 15;209(10):1591-601. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit677. Epub 2013 Dec 2. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24302757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey, J. R., H. Zhang, B. W. Wegweiser, H. C. Yang, L. Herrera, A. Ahonkhai, T. M. Williams, R. F. Siliciano, and J. N. Blankson. 2007. Evolution of HIV-1 in an HLA-B*57-positive patient during virologic escape. J. Infect. Dis. 196:50-55. - PubMed
-
- Betser-Cohen, G., G. Katz, T. Gonen-Gross, N. Stern, T. I. Arnon, H. Achdout R. Gazit, and O. Mandelboim. 2006. Reduced KIR2DL1 recognition of MHC class I molecules presenting phosphorylated peptides. J. Immunol. 176:6762-6769. - PubMed
-
- Biassoni, R. 2008. Natural killer cell receptors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 640:35-52. - PubMed
-
- Bottino, C., M. Vitale, D. Pende, R. Biassoni, and A. Moretta. 1995. Receptors for HLA class I molecules in human NK cells. Semin. Immunol. 7:67-73. - PubMed
-
- Byers, A. M., C. C. Kemball, N. P. Andrews, and A. E. Lukacher. 2003. Regulation of antiviral CD8+ T cells by inhibitory natural killer cell receptors. Microbes Infect. 5:169-177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

