Development of a drug-disease simulation model for rituximab in follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- PMID: 19843059
- PMCID: PMC2780281
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03494.x
Development of a drug-disease simulation model for rituximab in follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Abstract
Aim: Rituximab has dramatically improved the survival of patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHL), but the dosing regimen currently used should be optimized. However, the concentration-effect relationship of rituximab has never been described by pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) modelling, precluding the simulation of new dosing regimens. The aim of this study was to develop a PK-PD model of rituximab in relapsed/resistant follicular NHL (FL).
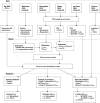
Methods: A model describing the relationship between rituximab concentrations and progression-free survival (PFS) was developed using data extracted from the pivotal study, which evaluated 151 relapsed/resistant FL patients. The influence of FCGR3A genetic polymorphism on the efficacy of rituximab was quantified using data from 87 relapsed/resistant FL patients. The predictive performance of the model was analysed using two independent datasets: a study that evaluated rituximab combined with chemotherapy [rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, adriamycin and prednisone (R-CHOP)] in 334 relapsed/resistant FL patients and a study that evaluated rituximab monotherapy in 47 asymptomatic FL patients with known FCGR3A genotype.
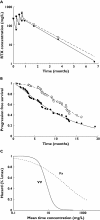
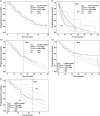
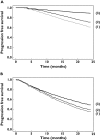
Results: For R-CHOP, observed and model-predicted PFS (90% confidence interval) at 24 months were 0.50 and 0.48 (0.40, 0.56), respectively, for the observation arm, and 0.62 and 0.59 (0.50, 0.65), respectively, for the rituximab maintenance arm. For rituximab monotherapy, observed and predicted PFS at 24 months were 0.67 and 0.63, respectively, for FCGR3A-V/V patients, and 0.41 and 0.36 (0.25, 0.49), respectively, for FCGR3A-F carriers.
Conclusions: Our model provides a satisfactory prediction of PFS at 24 months. It can be used to simulate new dosing regimens of rituximab in populations of FL patients and should improve the design of future clinical trials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, low-grade or follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Drugs. 2010 Jul 30;70(11):1445-76. doi: 10.2165/11201110-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20614951 Review.
-
Model-based design of rituximab dosage optimization in follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;73(4):597-605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04125.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21999172 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab maintenance treatment of relapsed/resistant follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: long-term outcome of the EORTC 20981 phase III randomized intergroup study.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Jun 10;28(17):2853-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.5827. Epub 2010 May 3. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20439641 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rituximab for the first-line treatment of stage III-IV follicular lymphoma (review of Technology Appraisal No. 110): a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(37):1-253, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta16370. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 23021127 Review.
-
Bendamustine plus rituximab versus R-CHOP as first-line treatment for patients with indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: evidence from a multicenter, retrospective study.Ann Hematol. 2016 Jun;95(7):1107-14. doi: 10.1007/s00277-016-2668-0. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Ann Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27103007
Cited by
-
Mechanism-based approach to the economic evaluation of pharmaceuticals: pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic/pharmacoeconomic analysis of rituximab for follicular lymphoma.Pharmacoeconomics. 2012 May;30(5):413-29. doi: 10.2165/11591540-000000000-00000. Pharmacoeconomics. 2012. PMID: 22428718
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, low-grade or follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Drugs. 2010 Jul 30;70(11):1445-76. doi: 10.2165/11201110-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20614951 Review.
-
Rituximab resistance.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2011 Jun;24(2):203-16. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2011.02.009. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2011. PMID: 21658619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postulated mechanisms of resistance of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma to rituximab treatment regimens: strategies to overcome resistance.Semin Oncol. 2014 Oct;41(5):667-77. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Semin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25440611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Resistance to Rituximab Used for the Treatment of Autoimmune Blistering Diseases.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;14(10):1223. doi: 10.3390/life14101223. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coiffier B, Haioun C, Ketterer N, Engert A, Tilly H, Ma D, Johnson P, Lister A, Feuring-Buske M, Radford JA, Capdeville R, Diehl V, Reyes F. Rituximab anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of patients with relapsing or refractory aggressive lymphoma: a multicenter phase II study. Blood. 1998;92:1927–32. - PubMed
-
- Maloney DG, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, Bodkin D, Schilder RJ, Neidhart JA, Janakiraman N, Foon KA, Liles TM, Dallaire BK, Wey K, Royston I, Davis T, Levy R. IDEC-C2B8 (Rituximab) anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in patients with relapsed low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood. 1997;90:2188–95. - PubMed
-
- Cartron G, Blasco H, Paintaud G, Watier H, Le Guellec C. Pharmacokinetics of rituximab and its clinical use: thought for the best use? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007;62:43–52. - PubMed
-
- Aviles A, Leon MI, Diaz-Maqueo JC, Garcia EL, Cleto S, Neri N. Rituximab in the treatment of refractory follicular lymphoma – six doses are better than four. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2001;10:313–6. - PubMed
-
- Bremer K. Semi-extended, six weekly rituximab infusions in pre-treated advanced low-grade B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a phase II study. Anticancer Drugs. 2003;14:809–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

