Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless
- PMID: 19837038
- PMCID: PMC2785045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.051
Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless
Abstract
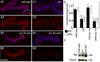
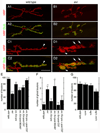
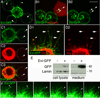
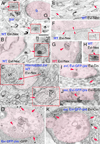
Wnts play pivotal roles during development and in the mature nervous system. However, the mechanism by which Wnts traffic between cells has remained elusive. Here we demonstrate a mechanism of Wnt transmission through release of exosome-like vesicles containing the Wnt-binding protein Evenness Interrupted/Wntless/Sprinter (Evi/Wls/Srt). We show that at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction (NMJ), presynaptic vesicular release of Evi is required for the secretion of the Wnt, Wingless (Wg). We also show that Evi acts cell-autonomously in the postsynaptic Wnt-receiving cell to target dGRIP, a Wg-receptor-interacting protein, to postsynaptic sites. Upon Evi loss of function, dGRIP is not properly targeted to synaptic sites, interfering with postsynaptic Wnt signal transduction. These findings uncover a previously unknown cellular mechanism by which a secreted Wnt is transported across synapses by Evi-containing vesicles and reveal trafficking functions of Evi in both the Wnt-producing and the Wnt-receiving cells. For a video summary of this article, see the PaperFlick file with the Supplemental Data available online.
Figures

Comment in
-
Ferrying wingless across the synaptic cleft.Cell. 2009 Oct 16;139(2):229-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.09.032. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19837027
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of evenness interrupted (Evi)-exosome release at synaptic boutons.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287(20):16820-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.342667. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22437826 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear trafficking of Drosophila Frizzled-2 during synapse development requires the PDZ protein dGRIP.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 16;103(20):7841-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600387103. Epub 2006 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16682643 Free PMC article.
-
Ferrying wingless across the synaptic cleft.Cell. 2009 Oct 16;139(2):229-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.09.032. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19837027
-
The role of Evi/Wntless in exporting Wnt proteins.Development. 2023 Feb 15;150(3):dev201352. doi: 10.1242/dev.201352. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Development. 2023. PMID: 36763105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt trafficking: new insights into Wnt maturation, secretion and spreading.Traffic. 2010 Oct;11(10):1265-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01076.x. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20477987 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure, Distribution, and Function of Neuronal/Synaptic Spinules and Related Invaginating Projections.Neuromolecular Med. 2015 Sep;17(3):211-40. doi: 10.1007/s12017-015-8358-6. Epub 2015 May 26. Neuromolecular Med. 2015. PMID: 26007200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of postsynaptic retrograde signaling by presynaptic exosome release.Neuron. 2013 Mar 20;77(6):1039-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.01.013. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23522040 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles and intercellular communication within the nervous system.J Clin Invest. 2016 Apr 1;126(4):1198-207. doi: 10.1172/JCI81134. Epub 2016 Apr 1. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27035811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microvesicle-mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Promotes Interspecies Mammary Stem/Progenitor Cell Growth.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 18;291(47):24390-24405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.726117. Epub 2016 Oct 12. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27733685 Free PMC article.
-
Microscopic and biochemical monitoring of endosomal trafficking and extracellular vesicle secretion in an endogenous in vivo model.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 Sep;11(9):e12263. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12263. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022. PMID: 36103151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeg GH, Lin X, Khare N, Baumgartner S, Perrimon N. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are critical for the organization of the extracellular distribution of Wingless. Development. 2001;128:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Banziger C, Soldini D, Schutt C, Zipperlen P, Hausmann G, Basler K. Wntless, a conserved membrane protein dedicated to the secretion of Wnt proteins from signaling cells. Cell. 2006;125:509–522. - PubMed
-
- Bartscherer K, Pelte N, Ingelfinger D, Boutros M. Secretion of Wnt ligands requires Evi, a conserved transmembrane protein. Cell. 2006;125:523–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

