microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 19826040
- PMCID: PMC2763324
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1996
microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells
Abstract
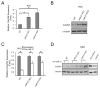
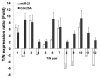
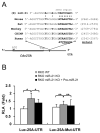
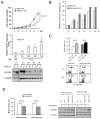
microRNAs (miRNA) are small noncoding RNAs that participate in diverse biological processes by suppressing target gene expression. Altered expression of miR-21 has been reported in cancer. To gain insights into its potential role in tumorigenesis, we generated miR-21 knockout colon cancer cells through gene targeting. Unbiased microarray analysis combined with bioinformatics identified cell cycle regulator Cdc25A as a miR-21 target. miR-21 suppressed Cdc25A expression through a defined sequence in its 3'-untranslated region. We found that miR-21 is induced by serum starvation and DNA damage, negatively regulates G(1)-S transition, and participates in DNA damage-induced G(2)-M checkpoint through down-regulation of Cdc25A. In contrast, miR-21 deficiency did not affect apoptosis induced by a variety of commonly used anticancer agents or cell proliferation under normal cell culture conditions. Furthermore, miR-21 was found to be underexpressed in a subset of Cdc25A-overexpressing colon cancers. Our data show a role of miR-21 in modulating cell cycle progression following stress, providing a novel mechanism of Cdc25A regulation and a potential explanation of miR-21 in tumorigenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-99a-5p suppresses breast cancer progression and cell-cycle pathway through downregulating CDC25A.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr;234(4):3526-3537. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26906. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30443946
-
MicroRNA 345, a methylation-sensitive microRNA is involved in cell proliferation and invasion in human colorectal cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Aug;32(8):1207-15. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr114. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21665895 Clinical Trial.
-
MicroRNA-184 Deregulated by the MicroRNA-21 Promotes Tumor Malignancy and Poor Outcomes in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer via Targeting CDC25A and c-Myc.Ann Surg Oncol. 2015 Dec;22 Suppl 3:S1532-9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4595-z. Epub 2015 May 20. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25990966
-
Functional screening identifies a microRNA, miR-491 that induces apoptosis by targeting Bcl-X(L) in colorectal cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2010 Sep 1;127(5):1072-80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25143. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20039318
-
The role of Cdc25A in the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 Jul;12(6):631-9. doi: 10.2174/187152012800617678. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22263797 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in the ionizing radiation response and in radiotherapy.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Feb;23(1):12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23453900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-21 Is a Promising Novel Biomarker for Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Gastric Cancer.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012;2012:640168. doi: 10.1155/2012/640168. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012. PMID: 22792096 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of miR-193a-3p regulates the apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by targeting PAK3.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Feb 15;14(2):1361-1375. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35273739 Free PMC article.
-
Serum microRNA-21 levels are related to tumor size in gastric cancer patients but cannot predict prognosis.Oncol Lett. 2013 Dec;6(6):1733-1737. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1626. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 24260069 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs in cancer cell response to ionizing radiation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jul 10;21(2):293-312. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5718. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24206455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- Kloosterman WP, Plasterk RH. The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev Cell. 2006;11:441–50. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8. - PubMed
-
- Nairz K, Rottig C, Rintelen F, Zdobnov E, Moser M, Hafen E. Overgrowth caused by misexpression of a microRNA with dispensable wild-type function. Dev Biol. 2006;291:314–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA106348-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121105-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121105/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129829-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA106348-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA116867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129829/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127590/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129829-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA106348-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA106348-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121105-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121105-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA106348/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA106348-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

