Reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) is necessary for macrophage infiltration and tissue repair
- PMID: 19805174
- PMCID: PMC2762666
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907359106
Reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) is necessary for macrophage infiltration and tissue repair
Abstract
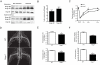
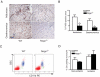
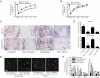
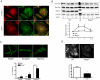
Blood vessel formation during ischemia and wound healing requires coordination of the inflammatory response with genes that regulate blood vessel assembly. Here we show that the reticulon family member 4B, aka Nogo-B, is upregulated in response to ischemia and is necessary for blood flow recovery secondary to ischemia and wound healing. Mice lacking Nogo-B exhibit reduced arteriogenesis and angiogenesis that are linked to a decrease in macrophage infiltration and inflammatory gene expression in vivo. Bone marrow-derived macrophages isolated from Nogo knock-out mice have reduced spreading and chemotaxis due to impaired Rac activation. Bone marrow reconstitution experiments show that Nogo in myeloid cells is necessary to promote macrophage homing and functional recovery after limb ischemia. Thus, endogenous Nogo coordinates macrophage-mediated inflammation with arteriogenesis, wound healing, and blood flow control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial reticulon-4B (Nogo-B) regulates ICAM-1-mediated leukocyte transmigration and acute inflammation.Blood. 2011 Feb 17;117(7):2284-95. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-281956. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21183689 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and regulation of reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) in renal tubular epithelial cells.Am J Pathol. 2010 Dec;177(6):2765-73. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100199. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20971739 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) is an endogenous regulator of Th2-driven lung inflammation.J Exp Med. 2010 Nov 22;207(12):2595-607. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100786. Epub 2010 Oct 25. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20975041 Free PMC article.
-
[Biological function of Nogo-B].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2013 Aug 25;65(4):445-50. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 23963076 Review. Chinese.
-
A Novel Role of Nogo Proteins: Regulating Macrophages in Inflammatory Disease.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;42(8):2439-2448. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01124-0. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34224050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophages in collateral arteriogenesis.Front Physiol. 2012 Sep 24;3:353. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00353. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23055975 Free PMC article.
-
Nogo-B receptor is essential for angiogenesis in zebrafish via Akt pathway.Blood. 2010 Dec 9;116(24):5423-33. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-271577. Epub 2010 Sep 2. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20813898 Free PMC article.
-
Reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) is a novel regulator of hepatic fibrosis.Hepatology. 2011 Apr;53(4):1306-15. doi: 10.1002/hep.24200. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21480333 Free PMC article.
-
The Nogo-B-PirB axis controls macrophage-mediated vascular remodeling.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 20;8(11):e81019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081019. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278366 Free PMC article.
-
MAP Kinase Phosphatase-5 Deficiency Protects Against Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 21;12:790511. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.790511. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34992607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oertle T, Schwab ME. Nogo and its paRTNers. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Teng FY, Tang BL. Cell autonomous function of Nogo and reticulons: The emerging story at the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Physiol. 2008;216:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Voeltz GK, Prinz WA, Shibata Y, Rist JM, Rapoport TA. A class of membrane proteins shaping the tubular endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 2006;124:573–586. - PubMed
-
- Shnyrova A, Frolov VA, Zimmerberg J. ER biogenesis: Self-assembly of tubular topology by protein hairpins. Curr Biol. 2008;18:R474–R476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

