Unusual thermal disassembly of the SPFH domain oligomer from Pyrococcus horikoshii
- PMID: 19804735
- PMCID: PMC2756375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.07.034
Unusual thermal disassembly of the SPFH domain oligomer from Pyrococcus horikoshii
Abstract
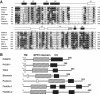
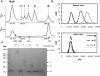
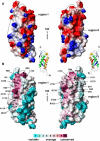
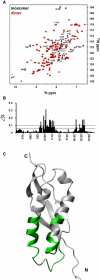
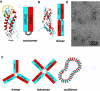
Stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH) domain proteins are membrane proteins that are widely conserved from bacteria to mammals. The molecular functions of these proteins have not been established. In mammals, the domain is often found in raft-associated proteins such as flotillin and podocin. We determined the structure of the SPFH domain of PH0470 derived from Pyrococcus horikoshii using NMR. The structure closely resembles that of the SPFH domain of the paralog PH1511, except for two C-terminal helices. The results show that the SPFH domain forms stable dimers, trimers, tetramers, and multimers, although it lacks the coiled-coil region for oligomerization, which is a highly conserved region in this protein family. The oligomers exhibited unusual thermodynamic behavior, as determined by circular dichroism, NMR, gel filtration, chemical cross-linking, and analytical ultracentrifugation. The oligomers were converted into monomers when they were heated once and then cooled. This transition was one-way and irreversible. We propose a mechanism of domain swapping for forming dimers as well as successive oligomers. The results of this study provide what to our knowledge are new insights into the common molecular function of the SPFH domain, which may act as a membrane skeleton through oligomerization by domain swapping.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural and mutational studies suggest key residues to determine whether stomatin SPFH domains form dimers or trimers.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Nov 11;32:101384. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101384. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36386441 Free PMC article.
-
¹H, ¹³C, and ¹⁵N resonance assignment of the SPFH domain of human stomatin.Biomol NMR Assign. 2012 Apr;6(1):23-5. doi: 10.1007/s12104-011-9317-2. Epub 2011 Jun 5. Biomol NMR Assign. 2012. PMID: 21643969
-
The lipid raft markers stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH)-domain proteins form an operon with NfeD proteins and function with apolar polyisoprenoid lipids.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020 Feb;46(1):38-48. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2020.1716682. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31983249 Review.
-
Crystal structure of a core domain of stomatin from Pyrococcus horikoshii Illustrates a novel trimeric and coiled-coil fold.J Mol Biol. 2008 Feb 22;376(3):868-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.12.024. Epub 2008 Jan 8. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18182167
-
[Three-dimensional structure of membrane protein stomatin and function of stomatin-specific protease].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Oct;130(10):1289-93. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.1289. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20930480 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Prohibitin overexpression predicts poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and invasion through ERK pathway activation in gallbladder cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Apr 16;35:68. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0346-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27084680 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, localization, and functional implications of the microdomain-forming stomatin family in the ciliated protozoan Paramecium tetraurelia.Eukaryot Cell. 2013 Apr;12(4):529-44. doi: 10.1128/EC.00324-12. Epub 2013 Feb 2. Eukaryot Cell. 2013. PMID: 23376944 Free PMC article.
-
Structural features and oligomeric nature of human podocin domain.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Jun 25;23:100774. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100774. eCollection 2020 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 32617419 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic marker and immunogenic membrane antigen: prohibitin (PHB) in pancreatic cancer.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 6;9(9):178. doi: 10.1038/s41424-018-0044-1. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30185797 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mutational studies suggest key residues to determine whether stomatin SPFH domains form dimers or trimers.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Nov 11;32:101384. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101384. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36386441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simons K., Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 1997;387:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Morrow I.C., Parton R.G. Flotillins and the PHB domain protein family: rafts, worms and anaesthetics. Traffic. 2005;6:725–740. - PubMed
-
- Tavernarakis N., Driscoll M., Kyrpides N.C. The SPFH domain: implicated in regulating targeted protein turnover in stomatins and other membrane-associated proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999;24:425–427. - PubMed
-
- Browman D.T., Hoegg M.B., Robbins S.M. The SPFH domain-containing proteins: more than lipid raft markers. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:394–402. - PubMed
-
- Salzer U., Prohaska R. Stomatin, flotillin-1, and flotillin-2 are major integral proteins of erythrocyte lipid rafts. Blood. 2001;97:1141–1143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

