Structure-based mechanism of ADP-ribosylation by sirtuins
- PMID: 19801667
- PMCID: PMC2785207
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.024521
Structure-based mechanism of ADP-ribosylation by sirtuins
Abstract
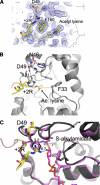
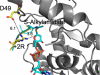
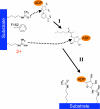
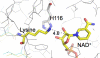
Sirtuins comprise a family of enzymes found in all organisms, where they play a role in diverse processes including transcriptional silencing, aging, regulation of transcription, and metabolism. The predominant reaction catalyzed by these enzymes is NAD(+)-dependent lysine deacetylation, although some sirtuins exhibit a weaker ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Although the Sir2 deacetylation mechanism is well established, much less is known about the Sir2 ADP-ribosylation reaction. We have studied the ADP-ribosylation activity of a bacterial sirtuin, Sir2Tm, and show that acetylated peptides containing arginine or lysine 2 residues C-terminal to the acetyl lysine, the +2 position, are preferentially ADP-ribosylated at the +2 residue. A structure of Sir2Tm bound to the acetylated +2 arginine peptide shows how this arginine could enter the active site and react with a deacetylation reaction intermediate to yield an ADP-ribosylated peptide. The new biochemical and structural studies presented here provide mechanistic insights into the Sir2 ADP-ribosylation reaction and will aid in identifying substrates of this reaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structural basis of sirtuin substrate affinity.Biochemistry. 2006 Jun 20;45(24):7511-21. doi: 10.1021/bi0526332. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16768447
-
Side chain specificity of ADP-ribosylation by a sirtuin.FEBS J. 2009 Dec;276(23):7159-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07427.x. Epub 2009 Nov 6. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19895577 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of sirtuins with NAD analogues and 32P-NAD.Biochemistry. 2009 Apr 7;48(13):2878-90. doi: 10.1021/bi802093g. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19220062
-
SIR2: the biochemical mechanism of NAD(+)-dependent protein deacetylation and ADP-ribosyl enzyme intermediates.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Apr;11(7):807-26. doi: 10.2174/0929867043455675. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15078167 Review.
-
Repairing split ends: SIRT6, mono-ADP ribosylation and DNA repair.Aging (Albany NY). 2011 Sep;3(9):829-35. doi: 10.18632/aging.100389. Aging (Albany NY). 2011. PMID: 21946623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Uncharacterized Components of Prokaryotic Immune Systems and Their Diverse Eukaryotic Reformulations.J Bacteriol. 2020 Nov 19;202(24):e00365-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00365-20. Print 2020 Nov 19. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32868406 Free PMC article.
-
Orthogonal Translation for Site-Specific Installation of Post-translational Modifications.Chem Rev. 2024 Mar 13;124(5):2805-2838. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00850. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 38373737 Review.
-
ADP-Ribosylation Post-Translational Modification: An Overview with a Focus on RNA Biology and New Pharmacological Perspectives.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 13;12(3):443. doi: 10.3390/biom12030443. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The natural history of ADP-ribosyltransferases and the ADP-ribosylation system.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;384:3-32. doi: 10.1007/82_2014_414. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25027823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genealogy of an ancient protein family: the Sirtuins, a family of disordered members.BMC Evol Biol. 2013 Mar 5;13:60. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-13-60. BMC Evol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23497088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frye R. A. (2000) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 273, 793–798 - PubMed
-
- Motta M. C., Divecha N., Lemieux M., Kamel C., Chen D., Gu W., Bultsma Y., McBurney M., Guarente L. (2004) Cell 116, 551–563 - PubMed
-
- Luo J., Nikolaev A. Y., Imai S., Chen D., Su F., Shiloh A., Guarente L., Gu W. (2001) Cell 107, 137–148 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

