Aplastic anemia: pathophysiology and treatment
- PMID: 19782144
- PMCID: PMC3521519
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.09.013
Aplastic anemia: pathophysiology and treatment
Abstract
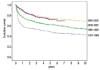
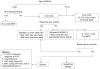
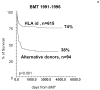
An immune basis for most patients with aplastic anemia (AA) provides a rationale for immunosuppressive therapy (IST), using antithmyocyte globulin and cyclosporine as one therapeutic modality; hematologic response is observed in up to 75% of patients. Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of AA have identified defective telomere maintenance as an important explanation for the onset of marrow failure, relapse and clonal evolution after IST, in some patients with AA. The finding of inherited mutations in the telomerase gene complex in patients with apparent acquired AA has important implications for clinical management. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for acquired AA, whether from an HLA identical sibling or an unrelated donor, provides an excellent chance of long term cure. Current issues with HSCT include graft rejection, chronic GVHD and poor outcome in older patients. The lack of a suitable bone marrow donor for all patients who need a transplant, illustrates the need for novel transplant procedures, such as cord blood transplantation.
Copyright 2010 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Making therapeutic decisions in adults with aplastic anemia.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006:78-85. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2006.1.78. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006. PMID: 17124044 Review.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of children with aplastic anemia.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2005 Nov;45(6):770-80. doi: 10.1002/pbc.20322. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15706582 Review.
-
Similar outcome of upfront-unrelated and matched sibling stem cell transplantation in idiopathic paediatric aplastic anaemia. A study on behalf of the UK Paediatric BMT Working Party, Paediatric Diseases Working Party and Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party of EBMT.Br J Haematol. 2015 Nov;171(4):585-94. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13614. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 26223288
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Aplastic Anemia.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Nov 16;18(12):70. doi: 10.1007/s11864-017-0511-z. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29143887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunosuppressive therapy for patients with Down syndrome and idiopathic aplastic anemia.Int J Hematol. 2016 Jul;104(1):130-3. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-1997-z. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Int J Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27107757
Cited by
-
[Acquired aplastic anemia developing myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia: clinical analysis of nineteen patients and literatures review].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Mar;36(3):216-20. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2015.03.009. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25854465 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Fibrosis and subsequent cytopenias are associated with basic fibroblast growth factor-deficient pluripotent mesenchymal stromal cells in large granular lymphocyte leukemia.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 1;191(7):3578-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203424. Epub 2013 Sep 6. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24014875 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to acquired aplastic anemia.Haematologica. 2015 Dec;100(12):1534-45. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2015.126128. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Haematologica. 2015. PMID: 26354756 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gene expression profiling identifies HOXB4 as a direct downstream target of GATA-2 in human CD34+ hematopoietic cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e40959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040959. Epub 2012 Sep 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028422 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-gamma and perforin-positive T cells in acquired aplastic anemia: implication in therapeutic response.Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 May 12;207(3):272-278. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxab006. Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35553631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fuhrer M. Risk-adapted procedures for HSCT from alternative donors in children with severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2008;42(Suppl 2):S97–100. - PubMed
-
- Locasciulli A, et al. Outcome of patients with acquired aplastic anemia given first line bone marrow transplantation or immunosuppressive treatment in the last decade: a report from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) Haematologica. 2007;92:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimi A, et al. Unrelated cord blood transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14:1057–1063. - PubMed
-
- Valdez JM, Scheinberg P, Young NS, Walsh TJ. Infections in patients with aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol. 2009;46:269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

