Regulation of proinflammatory cytokine expression in primary mouse astrocytes by coronavirus infection
- PMID: 19776127
- PMCID: PMC2786718
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01103-09
Regulation of proinflammatory cytokine expression in primary mouse astrocytes by coronavirus infection
Abstract
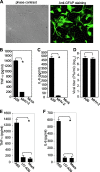
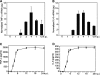
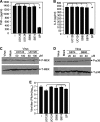
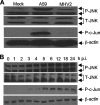
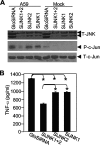
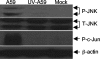
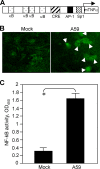
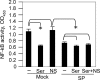
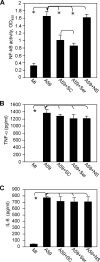
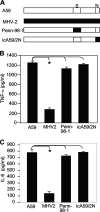
Previous studies have shown that proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), are differentially induced in primary mouse astrocytes by mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 (MHV-A59) and MHV-2. However, the signaling events that trigger TNF-alpha and IL-6 induction in these cells upon MHV infection remain unknown. In this study, we explored the potential signaling events. We found that induction of TNF-alpha and IL-6 occurred as early as 2 h postinfection and was completely dependent on viral replication. Using inhibitors specific for three mitogen-activated protein kinases, we showed that induction of TNF-alpha and IL-6 by MHV-A59 infection was mediated through activation of the Janus N-terminal kinase signaling pathway, but not through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase or p38 signaling pathway. This finding was further confirmed with knockdown experiments using small interfering RNAs specific for Janus N-terminal kinase. Interestingly, while nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), a key transcription factor required for the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in most cell types, was activated in astrocytes during MHV-A59 infection, disruption of the NF-kappaB pathway by peptide inhibitors did not significantly inhibit TNF-alpha and IL-6 expression. Furthermore, experiments using chimeric viruses demonstrated that the viral spike and nucleocapsid proteins, which play important roles in MHV pathogenicity in mice, are not responsible for the differential induction of the cytokines. These results illustrate the complexity of the regulatory mechanism by which MHV induces proinflammatory cytokines in primary astrocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Murine coronavirus replication-induced p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation promotes interleukin-6 production and virus replication in cultured cells.J Virol. 2002 Jun;76(12):5937-48. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.12.5937-5948.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12021326 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of transcription factor Egr-1 gene expression in astrocytoma cells by Murine coronavirus infection.Virology. 2006 Nov 25;355(2):152-63. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.07.012. Epub 2006 Sep 5. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16908043 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus induction of class I major histocompatibility complex expression in murine astrocytes is virus strain specific.J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):1013-23. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.1013. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 8064222 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha are induced by coronavirus fixation to Toll-like receptor 2/heparan sulphate receptors but not carcinoembryonic cell adhesion antigen 1a.Immunology. 2009 Sep;128(1 Suppl):e181-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02946.x. Epub 2009 Aug 4. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 19740307 Free PMC article.
-
MDA5 Is Critical to Host Defense during Infection with Murine Coronavirus.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(24):12330-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01470-15. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26423942 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway by coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus promotes apoptosis independently of c-Jun.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Dec 13;8(12):3215. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0053-0. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 29238080 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of DUSP6 impairs infectious bronchitis virus replication by negatively regulating ERK pathway and promoting apoptosis.Vet Res. 2021 Jan 11;52(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00866-x. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33431056 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral effects of ergosterol peroxide in a pig model of porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) infection involves modulation of apoptosis and tight junction in the small intestine.Vet Res. 2021 Jun 14;52(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00955-5. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34127062 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha/Beta Interferon (IFN-α/β) Signaling in Astrocytes Mediates Protection against Viral Encephalomyelitis and Regulates IFN-γ-Dependent Responses.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e01901-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01901-17. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29491163 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus-induced ER stress response and its involvement in regulation of coronavirus-host interactions.Virus Res. 2014 Dec 19;194:110-23. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 25304691 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bylund, J., K. L. MacDonald, K. L. Brown, P. Mydel, L. V. Collins, R. E. W. Hancock, and D. P. Speert. 2007. Enhanced inflammatory responses of chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes involve ROS-independent activation of NF-κB. Eur. J. Immunol. 37:1087-1096. - PubMed
-
- Chung, I. Y., J. Kwon, and E. N. Benveniste. 1992. Role of protein kinase C activity in tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression. Involvement at the transcriptional level. J. Immunol. 149:3894-3902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

