Theoretical considerations on the topological organization of receptor mosaics
- PMID: 19751189
- PMCID: PMC2949285
- DOI: 10.2174/138920309789630606
Theoretical considerations on the topological organization of receptor mosaics
Abstract
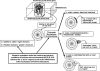
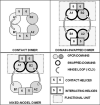
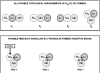
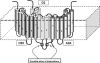
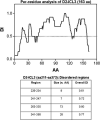
The concept of Receptor Mosaic (RM) is discussed; hence the integrative functions of the assemblage of G-protein coupled receptors physically interacting in the plane of the plasma membrane. The main focus is on a hetero-trimer of G-protein coupled receptors, namely the A2A-D2-CB1 receptor trimer. A bioinformatics analysis was carried out on the amino acid sequence of these receptors to indicate domains possibly involved in the receptor-receptor interactions. Such a bioinformatic analysis was also carried out on the RM formed by mGLU R5, D2 and A2A. The importance of topology, i.e., of the reciprocal localisation of the three interacting receptors in the plan of the membrane for the RM integrative functions is underlined. However, it is also pointed out that this fundamental aspect still waits techniques capable of an appropriate investigation. Finally, it is discussed how RM topology can give hints for a structural definition of the concept of hub receptor. Thus, just as in any network, the receptor operating as a hub is the one that in the molecular network formed by the receptors has the highest number of inputs.
Figures



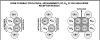
Similar articles
-
Brain receptor mosaics and their intramembrane receptor-receptor interactions: molecular integration in transmission and novel targets for drug development.J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2009 Mar;2(1):1-25. doi: 10.1016/S2005-2901(09)60011-X. Epub 2009 Apr 7. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2009. PMID: 20633470 Review.
-
Integrative action of receptor mosaics: relevance of receptor topology and allosteric modulators.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2008;28(6):543-65. doi: 10.1080/10799890802590420. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2008. PMID: 19096975 Review.
-
The changing world of G protein-coupled receptors: from monomers to dimers and receptor mosaics with allosteric receptor-receptor interactions.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010 Oct;30(5):272-83. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2010.506191. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010. PMID: 20684666 Review.
-
Receptor-receptor interactions: A novel concept in brain integration.Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Feb 9;90(2):157-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.10.004. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Prog Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 19850102
-
Moonlighting characteristics of G protein-coupled receptors: focus on receptor heteromers and relevance for neurodegeneration.IUBMB Life. 2011 Jul;63(7):463-72. doi: 10.1002/iub.473. IUBMB Life. 2011. PMID: 21698749 Review.
Cited by
-
mGlu5 Receptor Functional Interactions and Addiction.Front Pharmacol. 2012 May 7;3:84. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00084. eCollection 2012. Front Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22586398 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine, the less interactive cousin of arginine.Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2019 Apr;25(2):212-218. doi: 10.1177/1469066718791793. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester). 2019. PMID: 31018697 Free PMC article.
-
MALDI/post ionization-ion mobility mass spectrometry of noncovalent complexes of dopamine receptors' epitopes.J Proteome Res. 2013 Apr 5;12(4):1668-77. doi: 10.1021/pr301004w. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Proteome Res. 2013. PMID: 23469763 Free PMC article.
-
The dopamine D(4) receptor, the ultimate disordered protein.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010 Oct;30(5):331-6. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2010.513842. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010. PMID: 20836733 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Couplings and Molecular Dynamic Simulations Highlight Details of GPCRs Heterodimers' Interfaces.Molecules. 2023 Feb 15;28(4):1838. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041838. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agnati LF, Fuxe K. Subcortical limbic 3H-N-propylnorapomorphine binding sites are markedly modulated by cholecystokinin-8 in vitro. Biosci Rep. 1983;3:1101–1105. - PubMed
-
- Fuxe K, Agnati LF. Receptor-receptor interactions in the central nervous system: a new integrative mechanism in synapses. Med. Res. Rev. 1985;5:441–482. - PubMed
-
- Fuxe K, Agnati LF. Receptor-Receptor Interactions: a New Intramembrane Integrative Mechanism. MacMillan; London: 1987. pp. 14–18.
-
- Agnati LF, Ferré S, Lluis C, Franco R, Fuxe K. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutical implications of intramembrane receptor / receptor interactions among heptahelical receptors with examples from the striopallidal GABA neurons. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003;55:509–550. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Zoli M, Ozini I, Toffano G, Ferraguti F. A correlation analysis of the regional distribution of central enkephalin and beta-endorphin immunoreactive terminals and of opiate receptors in adult and old male rats: evidence for the existence of two main types of communication in the central nervous system: the volume transmission and the wiring transmission. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1986;128:201–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
