Mutant fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 induces intracellular signaling and cellular transformation in a cell type- and mutation-specific manner
- PMID: 19749790
- PMCID: PMC2789045
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.280
Mutant fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 induces intracellular signaling and cellular transformation in a cell type- and mutation-specific manner
Abstract
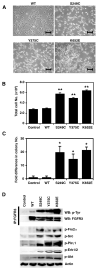
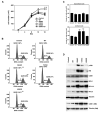
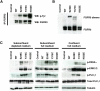
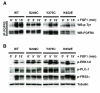
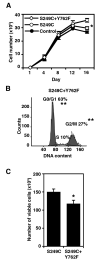
Although activating mutations of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) are frequent in bladder tumors, little information is available on their specific effects in urothelial cells or the basis for the observed mutation spectrum. We investigated the phenotypic and signaling consequences of three FGFR3 mutations (S249C, Y375C, and K652E) in immortalized normal human urothelial cells (TERT-NHUC) and mouse fibroblasts (NIH-3T3). In TERT-NHUC, all mutant forms of FGFR3 induced phosphorylation of FRS2alpha and ERK1/2, but not AKT or SRC. PLCgamma1 phosphorylation was only observed in TERT-NHUC expressing the common S249C and Y375C mutations, and not the rare K652E mutation. Cells expressing S249C and Y375C FGFR3 displayed an increased saturation density, related to increased proliferation and viability. This effect was significantly dependent on PLCgamma1 signaling and undetectable in cells expressing K652E FGFR3, which failed to phosphorylate PLCgamma1. In contrast to TERT-NHUC, expression of mutant FGFR3 in NIH-3T3 resulted in phosphorylation of Src and Akt. In addition, all forms of mutant FGFR3 were able to phosphorylate Plcgamma1 and induce morphological transformation, cell proliferation, and anchorage-independent growth. Our results indicate that the effects of mutant FGFR3 are both cell type specific and mutation specific. Mutant FGFR3 may confer a selective advantage in the urothelium by overcoming normal contact inhibition of proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockdown by shRNA identifies S249C mutant FGFR3 as a potential therapeutic target in bladder cancer.Oncogene. 2007 Aug 30;26(40):5889-99. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210399. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17384684 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 activation plays a causative role in urothelial cancer pathogenesis in cooperation with Pten loss in mice.J Pathol. 2014 Jun;233(2):148-58. doi: 10.1002/path.4334. Epub 2014 Mar 31. J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24519156 Free PMC article.
-
PIK3CA mutation spectrum in urothelial carcinoma reflects cell context-dependent signaling and phenotypic outputs.Oncogene. 2013 Feb 7;32(6):768-76. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.87. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22430209
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 in urothelial tumorigenesis.Urol Oncol. 2013 Apr;31(3):303-11. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.12.001. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Urol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22285006 Review.
-
Role of FGFR3 in urothelial cell carcinoma: biomarker and potential therapeutic target.World J Urol. 2007 Dec;25(6):581-93. doi: 10.1007/s00345-007-0213-4. Epub 2007 Oct 3. World J Urol. 2007. PMID: 17912529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Current knowledge in molecular pathology of urothelial cancer].Pathologe. 2010 Oct;31 Suppl 2:234-8. doi: 10.1007/s00292-010-1324-z. Pathologe. 2010. PMID: 20665023 Review. German.
-
Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity.Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Jan;15(1):25-41. doi: 10.1038/nrc3817. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25533674 Review.
-
FGF receptor inhibitors: role in cancer therapy.Curr Oncol Rep. 2012 Apr;14(2):111-9. doi: 10.1007/s11912-012-0225-0. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22311684 Review.
-
Case Report: PD-L1-negative advanced bladder cancer effectively treated with anlotinib and tislelizumab: A report of two cases.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 14;13:1164368. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1164368. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37124509 Free PMC article.
-
Unique signalling connectivity of FGFR3-TACC3 oncoprotein revealed by quantitative phosphoproteomics and differential network analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 25;8(61):102898-102911. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22048. eCollection 2017 Nov 28. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29262532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adar R, Monsonego-Ornan E, David P, Yayon A. Differential activation of cysteine-substitution mutants of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is determined by cysteine localization. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:860–868. - PubMed
-
- Agazie YM, Movilla N, Ischenko I, Hayman MJ. The phosphotyrosine phosphatase SHP2 is a critical mediator of transformation induced by the oncogenic fibroblast growth factor receptor 3. Oncogene. 2003;22:6909–6918. - PubMed
-
- Bernard-Pierrot I, Brams A, Dunois-Larde C, Caillault A, Diez de Medina SG, Cappellen D, et al. Oncogenic properties of the mutated forms of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3b. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:740–747. - PubMed
-
- Bonaventure J, Horne WC, Baron R. The localization of FGFR3 mutations causing thanatophoric dysplasia type I differentially affects phosphorylation, processing and ubiquitylation of the receptor. Febs J. 2007;274:3078–3093. - PubMed
-
- Cappellen D, De Oliveira C, Ricol D, de Medina S, Bourdin J, Sastre-Garau X, et al. Frequent activating mutations of FGFR3 in human bladder and cervix carcinomas. Nat Genet. 1999;23:18–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

