Fractalkine/CX3CL1 enhances GABA synaptic activity at serotonin neurons in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus
- PMID: 19748551
- PMCID: PMC2785445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.08.075
Fractalkine/CX3CL1 enhances GABA synaptic activity at serotonin neurons in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus
Erratum in
- Neuroscience. 2010 Feb 17;165(4):1559-60
Abstract
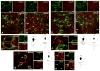
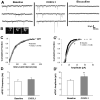
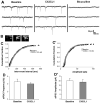
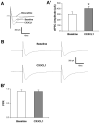
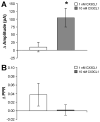
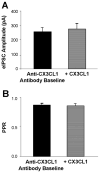
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) has an important role in mood regulation, and its dysfunction in the central nervous system (CNS) is associated with depression. Reports of mood and immune disorder co-morbidities indicate that immune-5-HT interactions may mediate depression present in immune compromised disease states including HIV/AIDS, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson's disease. Chemokines, immune proteins that induce chemotaxis and cellular adhesion, and their G-protein coupled receptors distribute throughout the CNS, regulate neuronal patterning, and mediate neuropathology. The purpose of this study is to investigate the neuroanatomical and neurophysiological relationship between the chemokine fractalkine/CX3CL1 and its receptor CX3CR1 with 5-HT neurons in the rat midbrain raphe nuclei (RN). Immunohistochemistry was used to examine the colocalization of CX3CL1 or CX3CR1 with 5-HT in the RN, and whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in rat brain slices were used to determine the functional impact of CX3CL1 on 5-HT dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) neurons. Greater than 70% of 5-HT neurons colocalize with CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 in the RN. CX3CL1 localizes as discrete puncta throughout the cytoplasm, whereas CX3CR1 concentrates to the perinuclear region of 5-HT neurons and exhibits microglial expression. CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 also colocalize with one another on individual RN cells. Electrophysiology studies indicate a CX3CL1-mediated enhancement of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic current (sIPSC) amplitude and dose-dependent increase of evoked IPSC (eIPSC) amplitude without affecting eIPSC paired-pulse ratio, a finding observed selectively in 5-HT neurons. CX3CL1's effect on eIPSC amplitude is blocked by pretreatment with an anti-CX3CL1 neutralizing antibody. Thus, CX3CL1 enhances postsynaptic GABA receptor number or sensitivity on 5-HT DRN neurons under conditions of both spontaneous and synaptically-evoked GABA release. CX3CL1 may indirectly inhibit 5-HT neurotransmission by increasing the sensitivity of 5-HT DRN neurons to GABA inputs. Therapies targeting CX3CL1 may treat serotonin related mood disorders, including depression experienced by patients with compromised immune systems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SDF-1alpha/CXCL12 enhances GABA and glutamate synaptic activity at serotonin neurons in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Feb;58(2):501-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.08.022. Epub 2009 Sep 13. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19755127 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin-releasing factor increases GABA synaptic activity and induces inward current in 5-hydroxytryptamine dorsal raphe neurons.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 26;28(48):12927-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2887-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19036986 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocretins (orexins) regulate serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus by excitatory direct and inhibitory indirect actions.J Neurosci. 2002 Nov 1;22(21):9453-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-21-09453.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12417670 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Role of CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) and Its Receptor CX3CR1 in Traumatic Brain and Spinal Cord Injury: Insight into Recent Advances in Actions of Neurochemokine Agents.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Apr;54(3):2167-2188. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9787-4. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26927660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of dorsal raphe nucleus serotonergic and non-serotonergic neurons, and of their receptors, in regulating waking and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.Sleep Med Rev. 2010 Oct;14(5):319-27. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2009.10.003. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Sleep Med Rev. 2010. PMID: 20153670 Review.
Cited by
-
Fractalkine/CX3CR1 axis is critical for neuroprotection induced by hypoxic postconditioning against cerebral ischemic injury.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 26;22(1):457. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01830-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39327578 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between GABAergic Neurotransmission and Inflammatory Cascades in the Post-ischemic Brain: Relevance for Stroke Recovery.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Mar 23;16:807911. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.807911. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35401118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuron-glia crosstalk in health and disease: fractalkine and CX3CR1 take centre stage.Open Biol. 2013 Dec 18;3(12):130181. doi: 10.1098/rsob.130181. Open Biol. 2013. PMID: 24352739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-γ acutely augments inhibition of neocortical layer 5 pyramidal neurons.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Feb 22;17(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-1722-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32087716 Free PMC article.
-
The prenatal challenge with lipopolysaccharide and polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid disrupts CX3CL1-CX3CR1 and CD200-CD200R signalling in the brains of male rat offspring: a link to schizophrenia-like behaviours.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Aug 23;17(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01923-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32829711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler MW, Rogers TJ. Are chemokines the third major system in the brain? J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:1204–1209. - PubMed
-
- Allen SJ, Crown SE, Handel TM. Chemokine: receptor structure, interactions, and antagonism. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:787–820. - PubMed
-
- Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Florio T, Schettini G. Chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2001;22:147–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

