In vitro and in vivo platelet targeting by cyclic RGD-modified liposomes
- PMID: 19743511
- PMCID: PMC2854838
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.32549
In vitro and in vivo platelet targeting by cyclic RGD-modified liposomes
Abstract
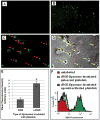
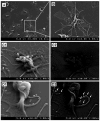
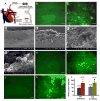
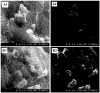
Cell-selective delivery using ligand-decorated nanoparticles is a promising modality for treating cancer and vascular diseases. We are developing liposome nanoparticles surface-modified by RGD peptide ligands having targeting specificity to integrin GPIIb-IIIa. This integrin is upregulated and stimulated into a ligand-binding conformation on the surface activated platelets. Activated-platelet adhesion and aggregation are primary events in atherosclerosois, thrombosis, and restenosis. Hence, platelet-targeted nanoparticles hold the promise of vascular site-selective delivery of drugs and imaging probes. Here, we report in vitro and ex vivo microscopy studies of platelet-targeting by liposomes surface-modified with a cyclic RGD peptide. The peptide-modified liposomes were labeled either with a lipophilic fluorophore or with lipid-tethered Nanogold(R). For in vitro tests, coverslip-adhered activated human platelets were incubated with probe-labeled liposomes, followed by analysis with fluorescence microscopy, phase contrast microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). For in vivo tests, the liposomes were introduced within a catheter-injured carotid artery restenosis model in rats and post-euthanasia, the artery was imaged ex vivo by fluorescence microscopy and SEM. All microscopy results showed successful platelet-targeting by the peptide-modified liposomes. The in vitro SEM results also enabled visualization of nanoscopic liposomes attached to activated platelets. The results validate our nanoparticle design for site-selective vascular delivery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Affinity manipulation of surface-conjugated RGD peptide to modulate binding of liposomes to activated platelets.Biomaterials. 2008 Apr;29(11):1676-85. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.12.015. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Biomaterials. 2008. PMID: 18192005 Free PMC article.
-
Heteromultivalent liposomal nanoconstructs for enhanced targeting and shear-stable binding to active platelets for site-selective vascular drug delivery.Biomaterials. 2011 Dec;32(35):9504-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.067. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21906806
-
RGD-modified liposomes targeted to activated platelets as a potential vascular drug delivery system.Thromb Haemost. 2005 Jan;93(1):106-14. doi: 10.1160/TH04-06-0340. Thromb Haemost. 2005. PMID: 15630499
-
Targeted delivery of thrombolytic agents: role of integrin receptors.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009 May;6(5):499-508. doi: 10.1517/17425240902878002. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009. PMID: 19413457 Review.
-
Radiation-mediated control of drug delivery.Am J Clin Oncol. 2001 Oct;24(5):473-80. doi: 10.1097/00000421-200110000-00012. Am J Clin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11586099 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle-Mediated Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 May 27;15:3741-3769. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S250872. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32547026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology, an alternative with promising prospects and advantages for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Nov 9;13:7349-7362. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S179678. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30519019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Strategies for Engineering Intravenous Hemostats.Bioconjug Chem. 2015 Jul 15;26(7):1224-36. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00070. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Bioconjug Chem. 2015. PMID: 25803791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trauma-targeted delivery of tranexamic acid improves hemostasis and survival in rat liver hemorrhage model.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Oct;17(10):1632-1644. doi: 10.1111/jth.14552. Epub 2019 Jul 15. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31220416 Free PMC article.
-
RAM, an RGDS analog, exerts potent anti-melanoma effects in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025352. Epub 2011 Oct 3. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21984914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michelson AD. Platelets. Academic Press; 2002.
-
- Munker R, Hiller E, Glass J, Paquette R. Biology and Clinical Management. Totowa, NJ: Humana; 2007. Modern Hematology.
-
- Ruggeri ZM. Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nature Medicine. 2002;8:1227–1234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

