Fenofibrate treatment increases human serum proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 levels
- PMID: 19738285
- PMCID: PMC2803236
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M000620
Fenofibrate treatment increases human serum proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 levels
Abstract
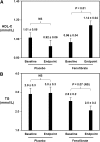
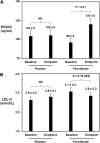
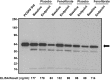
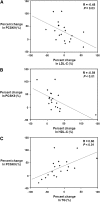
Over the past several years, proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) has gained significant attention as a key regulator of serum LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) levels. In humans, gain-of-function mutations in PCSK9 cause a form of familial hypercholesterolemia, whereas loss-of-function mutations result in significantly decreased LDL-C and cardiovascular risk. Our laboratory was the first to demonstrate that atorvastatin increases PCSK9 serum levels, an observation that has since been confirmed by at least two other groups. In light of these observations, we studied the effect of another common lipid-lowering medication, fenofibrate, on circulating PCSK9 protein levels in patients treated with fenofibrate or placebo for 12 weeks. We observed that fenofibrate (200 mg per day) significantly increased circulating PCSK9 levels by 25% compared with baseline. Placebo treatment, in comparison, had no effect on PCSK9 levels. Interestingly, fenofibrate-induced increases in serum PCSK9 levels were highly correlated with fenofibrate-induced changes in HDL-C and triglyceride levels, as well as with fenofibrate-induced changes in LDL-C levels. These results suggest an explanation for why fibrates do not achieve as much LDL-C lowering as might otherwise be expected and indicate that the addition of a PCSK9 inhibitor to fibrate therapy may result in additional beneficial LDL-C lowering.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of currently prescribed LDL-C-lowering drugs on PCSK9 and implications for the next generation of LDL-C-lowering agents.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Feb 28;10:38. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-38. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21352602 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin increases human serum levels of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9.J Lipid Res. 2008 Feb;49(2):394-8. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700437-JLR200. Epub 2007 Nov 21. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18033751
-
Plasma PCSK9 is increased by fenofibrate and atorvastatin in a non-additive fashion in diabetic patients.Atherosclerosis. 2010 Sep;212(1):246-51. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.05.027. Epub 2010 May 25. Atherosclerosis. 2010. PMID: 20619837 Clinical Trial.
-
Targeting the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 for the treatment of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;62(16):1401-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.056. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23973703 Review.
-
The next generation of novel low-density lipoprotein cholesterol-lowering agents: proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Jul;73:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23578522 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of currently prescribed LDL-C-lowering drugs on PCSK9 and implications for the next generation of LDL-C-lowering agents.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Feb 28;10:38. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-38. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21352602 Free PMC article.
-
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9: a new target molecule for gene therapy.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012 Jun;17(2):228-39. doi: 10.2478/s11658-012-0006-7. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22311433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCSK9 is present in human cerebrospinal fluid and is maintained at remarkably constant concentrations throughout the course of the day.Lipids. 2014 May;49(5):445-55. doi: 10.1007/s11745-014-3895-6. Lipids. 2014. PMID: 24659111
-
PCSK9 Mutations in Familial Hypercholesterolemia: from a Groundbreaking Discovery to Anti-PCSK9 Therapies.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017 Oct 17;19(12):49. doi: 10.1007/s11883-017-0684-8. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017. PMID: 29038906 Review.
-
Lipid Lowering Therapy and Circulating PCSK9 Concentration.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017 Sep 1;24(9):895-907. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17012. Epub 2017 Aug 14. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017. PMID: 28804094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cao G., Qian Y. W., Kowala M. C., Konrad R. J. 2008. Further LDL cholesterol lowering through targeting PCSK9 for coronary artery disease. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets. 8: 238–243. - PubMed
-
- Qian Y. W., Schmidt R. J., Zhang Y., Chu S., Lin A., Wang H., Wang X., Beyer T. P., Bensch W. R., Li W., et al. 2007. Secreted proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin-type 9 reduces low-density lipoprotein receptor through receptor-mediated endocytosis. J. Lipid Res. 48: 1488–1498. - PubMed
-
- Lambert G., Krempf M., Costet P. 2006. PCSK9: a promising therapeutic target for dyslipidemias. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 17: 79–81. - PubMed
-
- Graham M. J., Lemonidis K. M., Whipple C. P., Subramaniam A., Monia B. P., Crooke S. T., Crooke R. M. 2007. Antisense inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 reduces serum LDL in hyperlipidemic mice. J. Lipid Res. 48: 763–767. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

