Thymidine analog methods for studies of adult neurogenesis are not equally sensitive
- PMID: 19731267
- PMCID: PMC2749999
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22107
Thymidine analog methods for studies of adult neurogenesis are not equally sensitive
Abstract
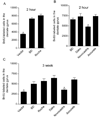
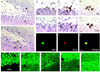
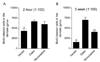
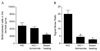
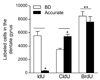
Adult neurogenesis is often studied by labeling new cells with the thymidine analog bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and using immunohistochemical methods for their visualization. Using this approach, considerable variability has been reported in the number of new cells produced in the dentate gyrus of adult rodents. We examined whether immunohistochemical methods, including BrdU antibodies from different vendors (Vector, BD, Roche, Dako, Novocastra, and Accurate) and DNA denaturation pretreatments alter the quantitative and qualitative patterns of BrdU labeling. We also compared the sensitivity and specificity of BrdU with two other thymidine analogs, iododeoxyuridine (IdU) and chlorodeoxyuridine (CldU). We found that the number of BrdU-labeled cells in the dentate gyrus of adult rats was dependent on the BrdU antibody used but was unrelated to differences in antibody penetration. Even at a higher concentration, some antibodies (Vector and Novocastra) stained fewer cells. A sensitive BrdU antibody (BD) was specific for dividing cells; all BrdU-labeled cells stained for Ki67, an endogenous marker of cell proliferation. We also observed that DNA denaturation pretreatments affected the number of BrdU-labeled cells and staining intensity for a marker of neuronal differentiation, NeuN. Finally, we found that IdU and CldU, when used at molarities comparable to those that label the maximal number of cells with BrdU, are less sensitive. These data suggest that antibody and thymidine analog selection, as well as the staining procedure employed, can affect the number of newly generated neurons detected in the adult brain, thus providing a potential explanation for some of the variability in the adult neurogenesis literature.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sustained increase in adult neurogenesis in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus after transient brain ischemia.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Jan 13;488(1):70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.10.079. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21056620
-
Low doses of bromo- and iododeoxyuridine produce near-saturation labeling of adult proliferative populations in the dentate gyrus.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Feb;21(3):803-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03907.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15733099
-
Systematic differences in time of cerebellar-neuron origin derived from bromodeoxyuridine immunoperoxidase staining protocols and tritiated thymidine autoradiography: A comparative study.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2015 Dec;47(Pt B):216-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26434379
-
BrdU immunohistochemistry for studying adult neurogenesis: paradigms, pitfalls, limitations, and validation.Brain Res Rev. 2007 Jan;53(1):198-214. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.08.002. Epub 2006 Oct 3. Brain Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 17020783 Review.
-
Endogenous versus exogenous markers of adult neurogenesis in canaries and other birds: advantages and disadvantages.J Comp Neurol. 2014 Dec 15;522(18):4100-20. doi: 10.1002/cne.23661. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Comp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25131458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Social isolation impairs adult neurogenesis in the limbic system and alters behaviors in female prairie voles.Horm Behav. 2012 Sep;62(4):357-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.03.005. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Horm Behav. 2012. PMID: 22465453 Free PMC article.
-
Fatherhood reduces the survival of adult-generated cells and affects various types of behavior in the prairie vole (Microtus ochrogaster ).Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Nov;38(9):3345-55. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12323. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23899240 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of doublecortin, a neuronal migration protein, in unipolar brush cells of the vestibulocerebellum and dorsal cochlear nucleus of the adult rat.Neuroscience. 2012 Jan 27;202:169-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.013. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22198017 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in contextual pattern separation, neurogenesis, and functional connectivity within the limbic system.Biol Sex Differ. 2022 Jul 23;13(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13293-022-00450-2. Biol Sex Differ. 2022. PMID: 35870952 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant and proneurogenic influence of environmental enrichment in mice: protective effects vs recovery.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 Nov;36(12):2460-8. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.134. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21796111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M. Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:523–569. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124:319–335. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis. I. A longitudinal investigation of the kinetics, migration and transformation of cells incorporating tritiated thymidine in neonate rats, with special reference to postnatal neurogenesis in some brain regions. J Comp Neurol. 1966;126:337–389. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Postnatal neurogenesis in the guinea-pig. Nature. 1967;214:1098–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

