Egr-1 is necessary for fibroblast growth factor-2-induced transcriptional activation of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in murine astrocytes
- PMID: 19721135
- PMCID: PMC2781613
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.010678
Egr-1 is necessary for fibroblast growth factor-2-induced transcriptional activation of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in murine astrocytes
Abstract
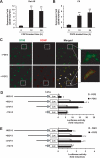
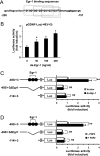
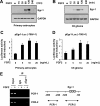
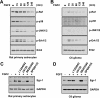
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (Gdnf) promotes neurite outgrowth and survival of neuronal cells, but its transcriptional regulation is poorly understood. Here, we sought to investigate the mechanism underlying fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2) induction of Gdnf expression in astrocytes. We found that FGF2 stimulation of rat astrocytes induced expression of Egr-1 at a high level. Sequence analysis of the rat Gdnf gene identified three overlapping Egr-1-binding sites between positions -185 and -163 of the rat Gdnf promoter. Transfection studies using a series of deleted Gdnf promoters revealed that these Egr-1-binding sites are required for maximal activation of the Gdnf promoter by FGF2. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis indicated that Egr-1 binds to the Gdnf promoter. Furthermore, the induction of Gdnf expression by FGF2 is strongly attenuated both in C6 glioma cells stably expressing Egr-1-specific small interfering RNA and in primary cultured astrocytes from the Egr-1 knock-out mouse. Additionally, we found that stimulation of the ERK and JNK pathways by FGF2 is functionally linked to Gdnf expression through the induction of Egr-1. These data demonstrate that FGF2-induced Gdnf expression is mediated by the induction of Egr-1 through activation of the ERK and JNK/Elk-1 signaling pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imipramine activates glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor via early growth response gene 1 in astrocytes.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Jun 1;35(4):1026-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2011.02.012. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21354245
-
Egr-1 participates in abnormally high gdnf gene transcription mediated by histone hyperacetylation in glioma cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Nov;1839(11):1161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.08.014. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25201174
-
[Increased Egr-1 binding to promoter induced by histone hyperacetylation promotes gdnf gene transcription].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015 May;35(5):697-701. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26018265 Chinese.
-
Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Focal Ischemic Stroke.Neurochem Res. 2021 Oct;46(10):2638-2650. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03266-5. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33591443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor isoforms in human glial tumors.Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2022;86(6):106-112. doi: 10.17116/neiro202286061106. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2022. PMID: 36534631 Review. English, Russian.
Cited by
-
Dopamine D2 receptor activation leads to an up-regulation of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor via Gβγ-Erk1/2-dependent induction of Zif268.J Neurochem. 2013 Apr;125(2):193-204. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12178. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23373701 Free PMC article.
-
Egr-1 activation by cancer-derived extracellular vesicles promotes endothelial cell migration via ERK1/2 and JNK signaling pathways.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 12;9(12):e115170. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115170. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25502753 Free PMC article.
-
Tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline activates fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in glial cells: involvement in glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor production.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21118-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.224683. Epub 2011 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21515689 Free PMC article.
-
Testicular endothelial cells are a critical population in the germline stem cell niche.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 22;9(1):4379. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06881-z. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30348976 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleus RNA sequencing reveals glial cell type-specific responses to ischemic stroke.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 26:2023.12.26.573302. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.26.573302. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 24;15(1):6232. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50465-z. PMID: 38234821 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ullian E. M., Christopherson K. S., Barres B. A. (2004) Glia 47, 209–216 - PubMed
-
- Darlington C. L. (2005) Curr. Opin. Investig. Drug 6, 700–703 - PubMed
-
- Lin L. F., Doherty D. H., Lile J. D., Bektesh S., Collins F. (1993) Science 260, 1130–1132 - PubMed
-
- Pozas E., Ibáñez C. F. (2005) Neuron 45, 701–713 - PubMed
-
- Moore M. W., Klein R. D., Fariñas I., Sauer H., Armanini M., Phillips H., Reichardt L. F., Ryan A. M., Carver-Moore K., Rosenthal A. (1996) Nature 382, 76–79 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

