Activation of hormone-sensitive lipase requires two steps, protein phosphorylation and binding to the PAT-1 domain of lipid droplet coat proteins
- PMID: 19717842
- PMCID: PMC2797282
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.006726
Activation of hormone-sensitive lipase requires two steps, protein phosphorylation and binding to the PAT-1 domain of lipid droplet coat proteins
Abstract
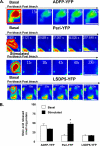
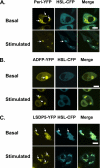
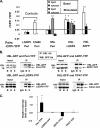
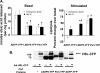
Lipolysis is an important metabolic pathway controlling energy homeostasis through degradation of triglycerides stored in lipid droplets and release of fatty acids. Lipid droplets of mammalian cells are coated with one or more members of the PAT protein family, which serve important functions in regulating lipolysis. In this study, we investigate the mechanisms by which PAT family members, perilipin A, adipose differentiation-related protein (ADFP), and LSDP5, control lipolysis catalyzed by hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), a major lipase in adipocytes and several non-adipose cells. We applied fluorescence microscopic tools to analyze proteins in situ in cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching and anisotropy Forster resonance energy transfer. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching data show that ADFP and LSDP5 exchange between lipid droplet and cytoplasmic pools, whereas perilipin A does not. Differences in protein mobility do not correlate with PAT protein-mediated control of lipolysis catalyzed by HSL or endogenous lipases. Forster resonance energy transfer and co-immunoprecipitation experiments reveal that each of the three PAT proteins bind HSL through interaction of the lipase with amino acids within the highly conserved amino-terminal PAT-1 domain. ADFP and LSDP5 bind HSL under basal conditions, whereas phosphorylation of serine residues within three amino-terminal protein kinase A consensus sequences of perilipin A is required for HSL binding and maximal lipolysis. Finally, protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of HSL increases lipolysis in cells expressing ADFP or LSDP5; in contrast, phosphorylation of perilipin A exerts the major control over HSL-mediated lipolysis when perilipin is the main lipid droplet protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unique regulation of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) by perilipin 5, a lipid droplet-associated protein.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 6;286(18):15707-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.207779. Epub 2011 Mar 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21393244 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction of hormone-sensitive lipase and perilipin in lipolysis.J Lipid Res. 2009 Nov;50(11):2306-13. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M900176-JLR200. Epub 2009 Jun 10. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19515989 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin A is essential for the translocation of hormone-sensitive lipase during lipolytic activation.J Cell Biol. 2003 Jun 23;161(6):1093-103. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200210169. Epub 2003 Jun 16. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12810697 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PAT proteins in lipid metabolism.Biochimie. 2005 Jan;87(1):45-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.12.010. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 15733736 Review.
-
The central role of perilipin a in lipid metabolism and adipocyte lipolysis.IUBMB Life. 2004 Jul;56(7):379-85. doi: 10.1080/15216540400009968. IUBMB Life. 2004. PMID: 15545214 Review.
Cited by
-
Hormone-sensitive lipase protects adipose triglyceride lipase-deficient mice from lethal lipotoxic cardiomyopathy.J Lipid Res. 2022 May;63(5):100194. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100194. Epub 2022 Mar 11. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 35283217 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi screening for fat regulatory genes with SRS microscopy.Nat Methods. 2011 Feb;8(2):135-8. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1556. Epub 2011 Jan 16. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21240281 Free PMC article.
-
Unique regulation of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) by perilipin 5, a lipid droplet-associated protein.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 6;286(18):15707-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.207779. Epub 2011 Mar 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21393244 Free PMC article.
-
Hormone signaling linked to silkmoth sex pheromone biosynthesis involves Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of the insect PAT family protein Bombyx mori lipid storage droplet protein-1 (BmLsd1).J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 8;286(27):24101-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.250555. Epub 2011 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21572162 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing the lipid droplet proteome: Mechanisms of lipid droplet protein targeting and degradation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Oct;1862(10 Pt B):1166-1177. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28627435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brasaemle D. L., Dolios G., Shapiro L., Wang R. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 46835–46842 - PubMed
-
- Liu P., Ying Y., Zhao Y., Mundy D. I., Zhu M., Anderson R. G. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 3787–3792 - PubMed
-
- Wu C. C., Howell K. E., Neville M. C., Yates J. R., 3rd, McManaman J. L. (2000) Electrophoresis 21, 3470–3482 - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto Y., Itabe H., Sakai J., Makita M., Noda J., Mori M., Higashi Y., Kojima S., Takano T. (2004) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1644, 47–59 - PubMed
-
- Ozeki S., Cheng J., Tauchi-Sato K., Hatano N., Taniguchi H., Fujimoto T. (2005) J. Cell Sci. 118, 2601–2611 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

