Coincidence of neurokinin 1 receptor with the vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (VGLUT3) in the rat forebrain
- PMID: 19699779
- PMCID: PMC2859883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.08.042
Coincidence of neurokinin 1 receptor with the vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (VGLUT3) in the rat forebrain
Abstract
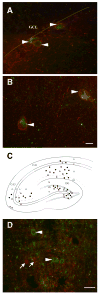
The third vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT3) is expressed in a subset of cholinergic and GABAergic neurons in the forebrain. In this study the distribution of VGLUT3 was mapped in relation to the receptor for substance P, neurokinin 1 (NK1), which has been independently reported within cholinergic and GABAergic neurons in a similar distribution. Dual immunofluorescence labeling techniques were used, sometimes in combination with triple labeling for the vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT), to identify cholinergic cells. Virtually all cells immunolabeled for VGLUT3 in the nucleus accumbens core and shell regions, ventral pallidum, olfactory tubercle and caudate putamen were cholinergic and also contained immunolabeling for the NK1 receptor. In the hippocampal formation where VGLUT3 has been described in GABAergic neurons, colocalization between NK1 and VGLUT3 was also common but less complete. Cells double labeled for NK1 and VGLUT3 were most prevalent in stratum radiatum in the CA1 subfield. In the habenula VGLUT3 was also found within NK1 receptor immunolabeled neurons. However, there were some areas where neurons containing these two proteins were separate populations including the cerebral cortex and median raphe nucleus. These results reveal a trend for VGLUT3 to localize within neurons containing the NK1 receptor in several areas of the forebrain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Locally collateralizing glutamate neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus responsive to substance P contain vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (VGLUT3).J Chem Neuroanat. 2009 Dec;38(4):273-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2009.05.005. Epub 2009 May 23. J Chem Neuroanat. 2009. PMID: 19467322 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular glutamate transporter 3 immunoreactivity is present in cholinergic basal forebrain neurons projecting to the basolateral amygdala in rat.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Oct 10;498(5):690-711. doi: 10.1002/cne.21081. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16917846
-
Complementary distribution of type 1 cannabinoid receptors and vesicular glutamate transporter 3 in basal forebrain suggests input-specific retrograde signalling by cholinergic neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Oct;18(7):1979-92. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02898.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14622230
-
Glutamatergic drive of the dorsal raphe nucleus.J Chem Neuroanat. 2011 Jul;41(4):247-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2011.04.004. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Chem Neuroanat. 2011. PMID: 21550397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diverse roles of vesicular glutamate transporter 3.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;(175):137-50. doi: 10.1007/3-540-29784-7_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16722234 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging targets for addiction neuropharmacology: From mechanisms to therapeutics.Prog Brain Res. 2016;224:251-84. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Prog Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26822362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative analysis of glutamatergic innervation of the mouse dorsal raphe nucleus using array tomography.J Comp Neurol. 2011 Dec 15;519(18):3802-14. doi: 10.1002/cne.22734. J Comp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21800318 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol and nicotine interaction within the posterior ventral tegmental area in male and female alcohol-preferring rats: evidence of synergy and differential gene activation in the nucleus accumbens shell.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Feb;232(3):639-49. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3702-3. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25155311 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-related neuropeptides and addictive behaviors: beyond the usual suspects.Neuron. 2012 Oct 4;76(1):192-208. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.026. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23040815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular architecture and transmitter phenotypes of neurons of the mouse median raphe region.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Jan;222(1):287-299. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1217-x. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 27044051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acsady L, Katona I, Gulyas AI, Shigemoto R, Freund TF. Immunostaining for substance P receptor labels GABAergic cells with distinct termination patterns in the hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 1997;378:320–336. - PubMed
-
- Arvidsson U, Riedl M, Elde R, Meister B. Vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) protein: a novel and unique marker for cholinergic neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems. J Comp Neurol. 1997;378:454–467. - PubMed
-
- Fremeau RT, Jr, Burman J, Qureshi T, Tran CH, Proctor J, Johnson J, Zhang H, Sulzer D, Copenhagen DR, Storm-Mathisen J, Reimer RJ, Chaudhry FA, Edwards RH. The identification of vesicular glutamate transporter 3 suggests novel modes of signaling by glutamate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:14488–14493. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fremeau RT, Jr, Troyer MD, Pahner I, Nygaard GO, Tran CH, Reimer RJ, Bellocchio EE, Fortin D, Storm-Mathisen J, Edwards RH. The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters defines two classes of excitatory synapse. Neuron. 2001;31:247–260. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

