A review of lipidomic technologies applicable to sphingolipidomics and their relevant applications
- PMID: 19690629
- PMCID: PMC2727941
- DOI: 10.1002/ejlt.200800117
A review of lipidomic technologies applicable to sphingolipidomics and their relevant applications
Abstract
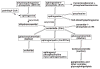
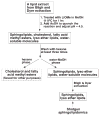
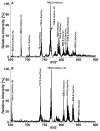
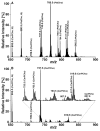
Sphingolipidomics, a branch of lipidomics, focuses on the large-scale study of the cellular sphingolipidomes. In the current review, two main approaches for the analysis of cellular sphingolipidomes (i.e. LC-MS- or LC-MS/MS-based approach and shotgun lipidomics-based approach) are briefly discussed. Their advantages, some considerations of these methods, and recent applications of these approaches are summarized. It is the authors' sincere hope that this review article will add to the readers understanding of the advantages and limitations of each developed method for the analysis of a cellular sphingolipidome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

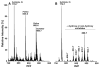
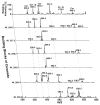
Similar articles
-
Shotgun lipidomics: electrospray ionization mass spectrometric analysis and quantitation of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2005 May-Jun;24(3):367-412. doi: 10.1002/mas.20023. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2005. PMID: 15389848 Review.
-
Mass Spectrometry-based Lipidomics and Its Application to Biomedical Research.J Lifestyle Med. 2014 Mar;4(1):17-33. doi: 10.15280/jlm.2014.4.1.17. Epub 2014 Mar 31. J Lifestyle Med. 2014. PMID: 26064851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-specific, quantitative methods for analysis of sphingolipids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: "inside-out" sphingolipidomics.Methods Enzymol. 2007;432:83-115. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)32004-1. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17954214
-
Analytical methods in sphingolipidomics: Quantitative and profiling approaches in food analysis.J Chromatogr A. 2016 Jan 8;1428:16-38. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.110. Epub 2015 Aug 1. J Chromatogr A. 2016. PMID: 26275862 Review.
-
Sphingolipidomics analysis of large clinical cohorts. Part 2: Potential impact and applications.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 7;504(3):602-607. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.075. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29654757 Review.
Cited by
-
Distribution and functions of sterols and sphingolipids.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 May 1;3(5):a004762. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a004762. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21454248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shotgun lipidomics in substantiating lipid peroxidation in redox biology: Methods and applications.Redox Biol. 2017 Aug;12:946-955. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.04.030. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28494428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Omics Approaches and Radiation on Lipid Metabolism in Toothed Whales.Life (Basel). 2021 Apr 20;11(4):364. doi: 10.3390/life11040364. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipidomics in Translational Sepsis Research-Biomedical Considerations and Perspectives.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 20;7:616578. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.616578. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33553212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the mass spectrometric analysis of glycosphingolipidome - A review.Anal Chim Acta. 2020 Oct 2;1132:134-155. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.05.051. Epub 2020 May 24. Anal Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32980104 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kiechle FL, Zhang X, Holland-Staley CA. The -omics era and its impact. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128:1337–1345. - PubMed
-
- Altman RB, Rubin DL, Klein TE. An “omics” view of drug development. Drug Dev Res. 2004;62:81–85.
-
- Duncan MW. Omics and its 15 minutes. Exp Biol Med. 2007;232:471–472. - PubMed
-
- Han X, Gross RW. Global analyses of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by ESI mass spectrometry: A bridge to lipidomics. J Lipid Res. 2003;44:1071–1079. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
