Domain analyses of the Runx1 transcription factor responsible for modulating T-cell receptor-beta/CD4 and interleukin-4/interferon-gamma expression in CD4(+) peripheral T lymphocytes
- PMID: 19689732
- PMCID: PMC2747135
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03042.x
Domain analyses of the Runx1 transcription factor responsible for modulating T-cell receptor-beta/CD4 and interleukin-4/interferon-gamma expression in CD4(+) peripheral T lymphocytes
Abstract
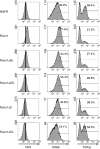
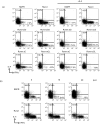
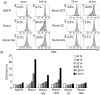
The Runx1 transcription factor is one of the master regulators of T-lymphocyte differentiation. There have been several reports trying to assign a domain within the Runx1 protein that is responsible for gene expression in thymocytes. The Runx1 domains involved in regulating the expression of several genes in peripheral CD4(+) T cells were analysed. It was observed that Runx1 over-expression enhanced the surface expression of CD4 and CD69 molecules via its activation domain and VWRPY domain, and decreased that of T-cell receptor-beta via its activation domain. Runx1 over-expression enhanced interferon-gamma expression via its activation and VWRPY domains, and abolished interleukin-4 expression through its activation domain. Transduction of Runx1 did not down-regulate CD4 expression until 72 hr of culture, but the repression of CD4 expression became evident after 96 hr. The main region responsible for repressing CD4 expression was the inhibitory domain of Runx1. Taken together, these results lead to a proposal that the regions in Runx1 responsible for modulating gene expression are distinct in thymocytes and in peripheral CD4(+) T cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional domains of Runx1 are differentially required for CD4 repression, TCRbeta expression, and CD4/8 double-negative to CD4/8 double-positive transition in thymocyte development.J Immunol. 2005 Mar 15;174(6):3526-33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.6.3526. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15749889
-
The artificial loss of Runx1 reduces the expression of quiescence-associated transcription factors in CD4(+) T lymphocytes.Mol Immunol. 2015 Dec;68(2 Pt A):223-33. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.08.012. Epub 2015 Sep 5. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26350416
-
Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits human antigen-specific CD4+ T cell proliferation without modulating the cytokine response.Int Immunol. 2003 Dec;15(12):1495-504. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxg147. Int Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14645158
-
Localization of the domains in Runx transcription factors required for the repression of CD4 in thymocytes.J Immunol. 2004 Apr 1;172(7):4359-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.7.4359. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15034051
-
Positive selection of thymocytes: the long and winding road.Immunol Today. 1999 Oct;20(10):463-8. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(99)01524-8. Immunol Today. 1999. PMID: 10500294 Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA FENDRR Expression Correlates with Tumor Immunogenicity.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 10;12(6):897. doi: 10.3390/genes12060897. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34200642 Free PMC article.
-
Specific subfamilies of transposable elements contribute to different domains of T lymphocyte enhancers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 7;117(14):7905-7916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1912008117. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32193341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kagoshima H, Shigesada K, Satake M, Ito Y, Miyoshi H, Ohki M, Pepling M, Gergen P. The Runt domain identifies a new family of heteromeric transcriptional regulators. Trends Genet. 1993;9:338–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

