Natural killer cell cytotoxicity: how do they pull the trigger?
- PMID: 19689731
- PMCID: PMC2747134
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03123.x
Natural killer cell cytotoxicity: how do they pull the trigger?
Abstract
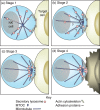
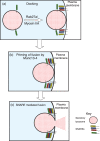
Natural killer (NK) cells target and kill aberrant cells, such as virally infected and tumorigenic cells. Killing is mediated by cytotoxic molecules which are stored within secretory lysosomes, a specialized exocytic organelle found in NK cells. Target cell recognition induces the formation of a lytic immunological synapse between the NK cell and its target. The polarized exocytosis of secretory lysosomes is then activated and these organelles release their cytotoxic contents at the lytic synapse, specifically killing the target cell. The essential role that secretory lysosome exocytosis plays in the cytotoxic function of NK cells is highlighted by immune disorders that are caused by the mutation of critical components of the exocytic machinery. This review will discuss recent studies on the molecular basis for NK cell secretory lysosome exocytosis and the immunological consequences of defects in the exocytic machinery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis and exocytosis of cytotoxic granules.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Aug;10(8):568-79. doi: 10.1038/nri2803. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20634814 Review.
-
Centriole polarisation to the immunological synapse directs secretion from cytolytic cells of both the innate and adaptive immune systems.BMC Biol. 2011 Jun 28;9:45. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-9-45. BMC Biol. 2011. PMID: 21711522 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory cytotoxic granule maturation and exocytosis require the effector protein hMunc13-4.Nat Immunol. 2007 Mar;8(3):257-67. doi: 10.1038/ni1431. Epub 2007 Jan 21. Nat Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17237785
-
Dynamin 2 regulates granule exocytosis during NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity.J Immunol. 2008 Nov 15;181(10):6995-7001. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.6995. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18981119 Free PMC article.
-
Cell biological steps and checkpoints in accessing NK cell cytotoxicity.Immunol Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;92(3):245-55. doi: 10.1038/icb.2013.96. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Immunol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24445602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The long road to TRAIL therapy: a TRAILshort detour.Oncotarget. 2021 Mar 30;12(7):589-591. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27902. eCollection 2021 Mar 30. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 33868580 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CAR-T and CAR-NK as cellular cancer immunotherapy for solid tumors.Cell Mol Immunol. 2024 Oct;21(10):1089-1108. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01207-0. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39134804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Prostate Cancer Using Intratumoral Cytotopically Modified Interleukin-15 Immunotherapy in a Syngeneic Murine Model.Immunotargets Ther. 2020 Jul 27;9:115-130. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S257443. eCollection 2020. Immunotargets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32802803 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-NK Cells in the Treatment of Solid Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 31;22(11):5899. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115899. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34072732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 12;23(8):4268. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084268. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457086 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wong P, Pamer EG. CD8 T cell responses to infectious pathogens. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:29–70. - PubMed
-
- Boon T, Cerottini JC, Van den Eynde B, van der Bruggen P, Van Pel A. Tumor antigens recognized by T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:337–65. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Lora A, Algarra I, Garrido F. MHC class I antigens, immune surveillance, and tumor immune escape. J Cell Physiol. 2003;195:346–55. - PubMed
-
- Moretta L, Biassoni R, Bottino C, Cantoni C, Pende D, Mingari MC, Moretta A. Human NK cells and their receptors. Microbes Infect. 2002;4:1539–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

