Lessons from X-chromosome inactivation: long ncRNA as guides and tethers to the epigenome
- PMID: 19684108
- PMCID: PMC2725936
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1811209
Lessons from X-chromosome inactivation: long ncRNA as guides and tethers to the epigenome
Abstract
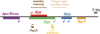
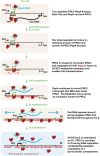
Transcriptome studies are revealing that the eukaryotic genome actively transcribes a diverse repertoire of large noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), many of which are unannotated and distinct from the small RNAs that have garnered much attention in recent years. Why are they so pervasive, and do they have a function? X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a classic epigenetic phenomenon associated with many large ncRNAs. Here, I provide a perspective on how XCI is achieved in mice and suggest how this knowledge can be applied to the rest of the genome. Emerging data indicate that long ncRNAs can function as guides and tethers, and may be the molecules of choice for epigenetic regulation: First, unlike proteins and small RNAs, large ncRNAs remain tethered to the site of transcription, and can therefore uniquely direct allelic regulation. Second, ncRNAs command a much larger sequence space than proteins, and can therefore achieve very precise spatiotemporal control of development. These properties imply that long noncoding transcripts may ultimately rival small RNAs and proteins in their versatility as epigenetic regulators, particularly for locus- and allele-specific control.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The X as model for RNA's niche in epigenomic regulation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Sep;2(9):a003749. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003749. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20739414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New twists in X-chromosome inactivation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;20(3):349-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.04.007. Epub 2008 May 26. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18508252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pluripotency factor Oct4 interacts with Ctcf and also controls X-chromosome pairing and counting.Nature. 2009 Jul 2;460(7251):128-32. doi: 10.1038/nature08098. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19536159 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-wide profiling of X-chromosome inactivation and epigenetic states in fetal brain and placenta of the opossum, Monodelphis domestica.Genome Res. 2014 Jan;24(1):70-83. doi: 10.1101/gr.161919.113. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24065774 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution analysis of epigenetic changes associated with X inactivation.Genome Res. 2009 Aug;19(8):1361-73. doi: 10.1101/gr.092643.109. Epub 2009 Jul 6. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19581487 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
NoRCE: non-coding RNA sets cis enrichment tool.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Jun 2;22(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04112-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34078267 Free PMC article.
-
The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome.Science. 2013 Aug 16;341(6147):1237973. doi: 10.1126/science.1237973. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Science. 2013. PMID: 23828888 Free PMC article.
-
A lncRNA regulates alternative splicing via establishment of a splicing-specific chromatin signature.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 May;22(5):370-6. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3005. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25849144 Free PMC article.
-
Stepwise de novo establishment of inactive X chromosome architecture in early development.Nat Genet. 2024 Oct;56(10):2185-2198. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01897-2. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 39256583
-
Non-coding RNAs: key regulators of mammalian transcription.Trends Biochem Sci. 2012 Apr;37(4):144-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012. PMID: 22300815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anguera MC, Sun BK, Xu N, Lee JT. X-chromosome kiss and tell: How the Xs go their separate ways. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:429–437. - PubMed
-
- Avner P, Heard E. X-chromosome inactivation: Counting, choice and initiation. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Bacher CP, Guggiari M, Brors B, Augui S, Clerc P, Avner P, Eils R, Heard E. Transient colocalization of X-inactivation centres accompanies the initiation of X inactivation. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:293–299. - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, West AG, Felsenfeld G. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell. 1999;98:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Allis CD. RNA meets chromatin. Genes & Dev. 2005;19:1635–1655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
